Glutamatergic enteric neurons
- PMID: 9169536
- PMCID: PMC6573355
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-12-04764.1997
Glutamatergic enteric neurons
Abstract
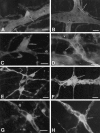
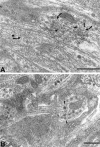
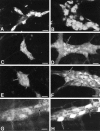
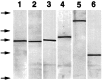
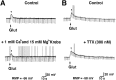
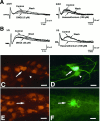
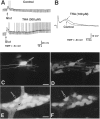
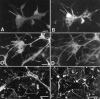
We tested the hypothesis that glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS, is also an excitatory neurotransmitter in the enteric nervous system (ENS). Glutamate immunoreactivity was found in cholinergic enteric neurons, many of which were identified as sensory by their co-storage of substance P and/or calbindin. Glutamate immunoreactivity was concentrated in terminal varicosities with a majority of small clear synaptic vesicles. The immunoreactivities of both AMPA and NMDA receptor subunits were also detected on neurons in both submucosal and myenteric plexuses. The immunoreactivity of the EAAC1 neuronal glutamate transporter was widespread in both plexuses. Glutamate evoked depolarizing responses in myenteric neurons that had fast and slow components. The fast component was mimicked by AMPA, and the slow component was mimicked by NMDA. The fast component and the response to AMPA mimicked fast EPSPs evoked in 2/AH neurons; moreover, fast EPSPs as well as fast glutamate and AMPA responses were blocked by selective AMPA antagonists and potentiated by the glutamate uptake inhibitor L-(-)-threo-3-hydroxyaspartic acid. These observations demonstrate, for the first time, the presence of glutamatergic neurons and glutamate-mediated neurotransmission in the ENS.
Figures






References
-
- Ascher P, Johnson JW. The NMDA receptor, its channel, and its modulation by glycine. In: Collingridge GL, Watkins JC, editors. The NMDA receptor. Oxford UP; Oxford: 1994. pp. 177–205.
-
- Balcar V, Johnston GAR, Twitchin B. Stereospecificity of the inhibition of l-glutamate and l-aspartate high affinity uptake in the rat brain by threo-3-hydroxyaspartate. J Neurochem. 1977;28:1145–1146. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand PP, Galligan JJ. Signal-transduction pathways causing slow synaptic excitation in guinea pig myenteric AH neurons. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G710–G720. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein J. Local neural control of intestinal motility: nerve circuits deduced for the guinea-pig small intestine. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1994;21:441–452. - PubMed
-
- Bornstein JC, Hendriks R, Furness JB, Trussell DC. Ramifications of the axons of AH-neurons injected with the intracellular marker biocytin in the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig small intestine. J Comp Neurol. 1991;314:437–451. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
