Crystal structure of heat shock locus V (HslV) from Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9177170
- PMCID: PMC21002
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6070
Crystal structure of heat shock locus V (HslV) from Escherichia coli
Abstract
Heat shock locus V (HslV; also called ClpQ) is the proteolytic core of the ATP-dependent protease HslVU in Escherichia coli. It has sequence similarity with the beta-type subunits of the eukaryotic and archaebacterial proteasomes. Unlike these particles, which display 72-point symmetry, it is a dimer of hexamers with 62-point symmetry. The crystal structure of HslV at 3.8-A resolution, determined by isomorphous replacement and symmetry averaging, shows that in spite of the different symmetry of the particle, the fold and the contacts between subunits are conserved. A tripeptide aldehyde inhibitor, acetyl-Leu-Leu-norleucinal, binds to the N-terminal threonine residue of HslV, probably as a hemiacetal, relating HslV also functionally to the proteasomes of archaea and eukaryotes.
Figures




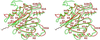
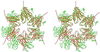

References
-
- Chuang S-E, Burland V, Plunkett G, III, Daniels D L, Blattner F R. Gene. 1993;134:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg A L. Eur J Biochem. 1992;203:9–23. - PubMed
-
- Schirmer E C, Glover J R, Singer M A, Lindquist S. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:289–296. - PubMed
-
- Zwickl P, Kleinz J, Baumeister W. Nat Struct Biol. 1994;1:765–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

