Induction by leptin of uncoupling protein-2 and enzymes of fatty acid oxidation
- PMID: 9177227
- PMCID: PMC21059
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.12.6386
Induction by leptin of uncoupling protein-2 and enzymes of fatty acid oxidation
Abstract
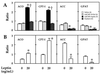
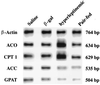
We have studied mechanisms by which leptin overexpression, which reduces body weight via anorexic and thermogenic actions, induces triglyceride depletion in adipocytes and nonadipocytes. Here we show that leptin alters in pancreatic islets the mRNA of the genes encoding enzymes of free fatty acid metabolism and uncoupling protein-2 (UCP-2). In animals infused with a recombinant adenovirus containing the leptin cDNA, the levels of mRNAs encoding enzymes of mitochondrial and peroxisomal oxidation rose 2- to 3-fold, whereas mRNA encoding an enzyme of esterification declined in islets from hyperleptinemic rats. Islet UCP-2 mRNA rose 6-fold. All in vivo changes occurred in vitro in normal islets cultured with recombinant leptin, indicating direct extraneural effects. Leptin overexpression increased UCP-2 mRNA by more than 10-fold in epididymal, retroperitoneal, and subcutaneous fat tissue of normal, but not of leptin-receptor-defective obese rats. By directly regulating the expression of enzymes of free fatty acid metabolism and of UCP-2, leptin controls intracellular triglyceride content of certain nonadipocytes, as well as adipocytes.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman J. Nature (London) 1994;372:425–432. - PubMed
-
- Pellymounter M A, Cullen M J, Baker M B, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F. Science. 1995;269:540–543. - PubMed
-
- Campfield L, Smith F, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P. Science. 1995;269:546–548. - PubMed
-
- Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley R E, Lee G H, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S, Kerm P S, Friedman J M. Nat Med. 1995;1:1155–1161. - PubMed
-
- Halaas J, Gajiwala K, Maffei M, Cohen S, Chait B, Rabinowitz D, Lallone R, Burley S. Science. 1995;269:543–546. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

