Redox modulation of hslo Ca2+-activated K+ channels
- PMID: 9185532
- PMCID: PMC6573296
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-13-04942.1997
Redox modulation of hslo Ca2+-activated K+ channels
Abstract
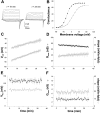
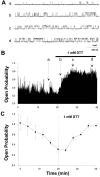
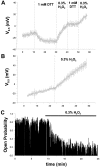
The modulation of ion channel proteins by cellular redox potential has emerged recently as a significant determinant of channel function. We have investigated the influence of sulfhydryl redox reagents on human brain Ca2+-activated K+ channels (hslo) expressed in both human embryonic kidney 293 cells and Xenopus oocytes using macropatch and single-channel analysis. Intracellular application of the reducing agent dithiothreitol (DTT): (1) shifts the voltage of half-maximal channel activation (V0.5) approximately 18 mV to more negative potentials without affecting the maximal conductance or the slope of the voltage dependence; (2) slows by approximately 10-fold a time-dependent right-shift in V0.5 values ("run-down"); (3) speeds macroscopic current activation kinetics by approximately 33%; and (4) increases the single-channel open probability without affecting the unitary conductance. In contrast to DTT treatment, oxidation with hydrogen peroxide shifts macropatch V0.5 values to more positive potentials, increases the rate of channel run-down, and decreases the single-channel open probability. KCa channels cloned from Drosophila differ from hslo channels in that they show very little run-down and are not modulated by the addition of DTT. These data indicate that hslo Ca2+-activated K+ channels may be modulated by changes in the cellular redox potential as well as by the transmembrane voltage and the cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration.
Figures





References
-
- Adelman J, Shen KZ, Kavanaugh MP, Warren RA, Wu YN, Lagrutta A, Bond CT, North RA. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complimentary DNAs. Neuron. 1992;9:209–216. - PubMed
-
- Aizenman E, Lipton SA, Loring RH. Selective modulation of NMDA responses by reduction and oxidation. Neuron. 1989;2:1257–1263. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson NS, Robertson GA, Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991;253:551–555. - PubMed
-
- Bielefeldt K, Jackson MB. A calcium-activated potassium channel causes frequency-dependent action potential failures in a mammalian nerve terminal. J Neurophysiol. 1993;458:41–67. - PubMed
-
- Bolotina VM, Najibi S, Palacino JJ, Pagano PJ, Cohen RA. Nitric oxide directly activated calcium-dependent potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle. Nature. 1994;368:850–853. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
