Chick ciliary ganglion neurons contain transcripts coding for acetylcholine receptor-associated protein at synapses (rapsyn)
- PMID: 9185539
- PMCID: PMC6573290
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-13-05016.1997
Chick ciliary ganglion neurons contain transcripts coding for acetylcholine receptor-associated protein at synapses (rapsyn)
Abstract
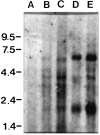
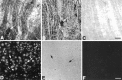
A peripheral membrane protein of approximately 43 kDa (rapsyn) clusters muscle nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChRs), but molecules relevant to clustering neuronal AChRs have not been identified. Here, we have detected rapsyn transcripts in the chick nervous system, localized rapsyn mRNA in ciliary ganglion (CG) neurons, which are known to cluster AChRs, and identified three rapsyn cDNAs derived from the ganglion. Our initial Northern blots, performed using a mouse probe, revealed rapsyn-like transcripts in chick muscle and brain. To develop species-specific probes, we prepared a chick rapsyn cDNA construct, Ch43K.1, that encodes a protein having extensive homology to mouse rapsyn. Using primers designed to anneal near the 5' and 3' boundaries of Ch43K.1, three prominent cDNAs were amplified from chick muscle templates by reverse transcriptase based-PCR. Products of similar size were also amplified using cDNA prepared from neuronal tissues expected to contain clustered AChRs (CG and brain), whereas none were detected using templates from tissues not displaying clustered AChRs (sensory ganglia and liver). In situ hybridization confirmed that rapsyn mRNA is expressed both in chick muscle fibers and in CG neurons. Sequencing the three cDNAs amplified from CG templates revealed the largest to be Ch43K.1, whereas the smaller two may represent splice variants. These findings suggest that multiple rapsyn-like molecules are involved in clustering the distinct AChRs expressed by muscle fibers and neurons.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Rapsyn variants in ciliary ganglia and their possible effects on clustering of nicotinic receptors.J Neurochem. 1999 Oct;73(4):1399-408. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0731399.x. J Neurochem. 1999. PMID: 10501183
-
Rapsyn clusters neuronal acetylcholine receptors but is inessential for formation of an interneuronal cholinergic synapse.J Neurosci. 1998 Jun 1;18(11):4166-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-11-04166.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9592096 Free PMC article.
-
Organizing effects of rapsyn on neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998 Apr;10(5-6):258-70. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1998.0664. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9604205
-
Innervation and target tissue interactions induce Rab-GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) expression during peripheral synapse formation in developing chick ciliary ganglion neurons in situ.J Neurosci. 1998 Aug 15;18(16):6331-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-16-06331.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9698324 Free PMC article.
-
An Inside Job: Molecular Determinants for Postsynaptic Localization of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors.Molecules. 2021 May 21;26(11):3065. doi: 10.3390/molecules26113065. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34063759 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CASK and FARP localize two classes of post-synaptic ACh receptors thereby promoting cholinergic transmission.PLoS Genet. 2022 Oct 24;18(10):e1010211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010211. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36279278 Free PMC article.
-
Abelson family tyrosine kinases regulate the function of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and nicotinic synapses on autonomic neurons.Mol Pharmacol. 2011 Jul;80(1):97-109. doi: 10.1124/mol.111.071308. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Mol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21502378 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane lipid rafts are necessary for the maintenance of the (alpha)7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in somatic spines of ciliary neurons.J Neurosci. 2001 Jan 15;21(2):504-12. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-02-00504.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11160430 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB signaling in parasympathetic neurons: relevance to regulating alpha7-containing nicotinic receptors and synaptic function.J Neurosci. 2004 May 5;24(18):4340-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0055-04.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15128848 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Rapsyn in neuromuscular junction and congenital myasthenic syndrome.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Sep 4;23(5):772-784. doi: 10.17305/bb.2022.8641. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 36815443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Apel ED, Merlie JP. Assembly of the postsynaptic apparatus. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995;5:62–67. - PubMed
-
- Auffray C, Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980;107:303–324. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin TJ, Theriot JA, Yoshihara CM, Burden SJ. Regulation of transcript encoding the 43K subsynaptic protein during development and after denervation. Development. 1988;104:557–564. - PubMed
-
- Betz H. Ligand-gated ion channels in the brain: the amino acid receptor superfamily. Neuron. 1990;5:383–392. - PubMed
-
- Boyd RT, Jacob MH, Couturier S, Ballivet M, Berg DK. Expression and regulation of neuronal acetylcholine receptor mRNA in chick ciliary ganglia. Neuron. 1988;1:495–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
