Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis
- PMID: 9185546
- PMCID: PMC6573293
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-13-05089.1997
Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis
Abstract
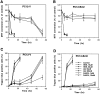
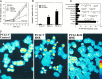
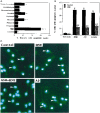
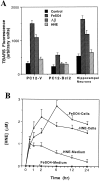
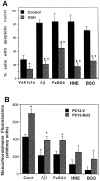
Oxidative stress is believed to play important roles in neuronal cell death associated with many different neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and cerebral ischemia), and it is believed also that apoptosis is an important mode of cell death in these disorders. Membrane lipid peroxidation has been documented in the brain regions affected in these disorders as well as in cell culture and in vivo models. We now provide evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE), an aldehydic product of membrane lipid peroxidation, is a key mediator of neuronal apoptosis induced by oxidative stress. HNE induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and primary rat hippocampal neurons. Oxidative insults (FeSO4 and amyloid beta-peptide) induced lipid peroxidation, cellular accumulation of HNE, and apoptosis. Bcl-2 prevented apoptosis of PC12 cells induced by oxidative stress and HNE. Antioxidants that suppress lipid peroxidation protected against apoptosis induced by oxidative insults, but not that induced by HNE. Glutathione, which binds HNE, protected neurons against apoptosis induced by oxidative stress and HNE. PC12 cells expressing Bcl-2 exhibited higher levels of glutathione and lower levels of HNE after oxidative stress. Collectively, the data identify that HNE is a novel nonprotein mediator of oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis and suggest that the antiapoptotic action of glutathione may involve detoxification of HNE.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson AJ, Pike CJ, Cotman CW. Differential induction of immediate early gene proteins in cultured neurons by β-amyloid (Aβ): association of c-Jun with Aβ-induced apoptosis. J Neurochem. 1995;65:1487–1498. - PubMed
-
- Ankarcrona M, Dypbukt JM, Bonfoco E, Zhivotovsky B, Orrenius S, Lipton SA, Nicotera P. Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron. 1995;15:961–973. - PubMed
-
- Barhoumi R, Bailey RH, Burghardt RC. Kinetic analysis of glutathione in anchored cells with monochlorobimane. Cytometry. 1995;19:226–234. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Ferrante RJ, Henshaw R, Matthews RT, Chan PH, Kowall NW, Epstein CJ, Schulz JB. 3-Nitropropionic acid neurotoxicity is attenuated in copper/zinc superoxide dismutase transgenic mice. J Neurochem. 1995;65:919–922. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
