Cross talk between adhesion molecules: control of N-cadherin activity by intracellular signals elicited by beta1 and beta3 integrins in migrating neural crest cells
- PMID: 9199179
- PMCID: PMC2137812
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.137.7.1663
Cross talk between adhesion molecules: control of N-cadherin activity by intracellular signals elicited by beta1 and beta3 integrins in migrating neural crest cells
Abstract
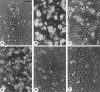
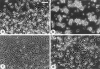
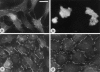
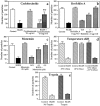
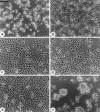
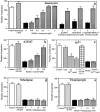
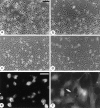
During embryonic development, cell migration and cell differentiation are associated with dynamic modulations both in time and space of the repertoire and function of adhesion receptors, but the nature of the mechanisms responsible for their coordinated occurrence remains to be elucidated. Thus, migrating neural crest cells adhere to fibronectin in an integrin-dependent manner while maintaining reduced N-cadherin-mediated intercellular contacts. In the present study we provide evidence that, in these cells, the control of N-cadherin may rely directly on the activity of integrins involved in the process of cell motion. Prevention of neural crest cell migration using RGD peptides or antibodies to fibronectin and to beta1 and beta3 integrins caused rapid N-cadherin-mediated cell clustering. Restoration of stable intercellular contacts resulted essentially from the recruitment of an intracellular pool of N-cadherin molecules that accumulated into adherens junctions in tight association with the cytoskeleton and not from the redistribution of a preexisting pool of surface N-cadherin molecules. In addition, agents that cause elevation of intracellular Ca2+ after entry across the plasma membrane were potent inhibitors of cell aggregation and reduced the N-cadherin- mediated junctions in the cells. Finally, elevated serine/ threonine phosphorylation of catenins associated with N-cadherin accompanied the restoration of intercellular contacts. These results indicate that, in migrating neural crest cells, beta1 and beta3 integrins are at the origin of a cascade of signaling events that involve transmembrane Ca2+ fluxes, followed by activation of phosphatases and kinases, and that ultimately control the surface distribution and activity of N-cadherin. Such a direct coupling between adhesion receptors by means of intracellular signals may be significant for the coordinated interplay between cell-cell and cell-substratum adhesion that occurs during embryonic development, in wound healing, and during tumor invasion and metastasis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Control of N-cadherin-mediated intercellular adhesion in migrating neural crest cells in vitro.J Cell Sci. 1995 Dec;108 ( Pt 12):3839-53. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.12.3839. J Cell Sci. 1995. PMID: 8719890
-
Beta3-integrins rather than beta1-integrins dominate integrin-matrix interactions involved in postinjury smooth muscle cell migration.Circulation. 1998 May 12;97(18):1818-27. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.97.18.1818. Circulation. 1998. PMID: 9603537
-
Cellular localization and signaling activity of beta-catenin in migrating neural crest cells.Dev Dyn. 2004 Aug;230(4):708-26. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20091. Dev Dyn. 2004. PMID: 15254905
-
Role of adhesion molecules in the genesis of the peripheral nervous system in avians.J Physiol (Paris). 1990;84(1):88-94. J Physiol (Paris). 1990. PMID: 2193150 Review.
-
Extracellular matrix receptors and the differentiation of human megakaryocytes in vitro.Leuk Lymphoma. 1999 Mar;33(1-2):15-23. doi: 10.3109/10428199909093721. Leuk Lymphoma. 1999. PMID: 10194117 Review.
Cited by
-
The desmosomal armadillo protein plakoglobin regulates prostate cancer cell adhesion and motility through vitronectin-dependent Src signaling.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e42132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042132. Epub 2012 Jul 30. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22860065 Free PMC article.
-
Tie2/TEK modulates the interaction of glioma and brain tumor stem cells with endothelial cells and promotes an invasive phenotype.Oncotarget. 2010 Dec;1(8):700-709. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.204. Oncotarget. 2010. PMID: 21321379 Free PMC article.
-
N-cadherin and β1 integrin coordinately regulate growth plate cartilage architecture.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Apr 1;35(4):ar49. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-03-0101. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38294852 Free PMC article.
-
The nonreceptor tyrosine kinase fer mediates cross-talk between N-cadherin and beta1-integrins.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jun 12;149(6):1263-74. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.6.1263. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10851023 Free PMC article.
-
NG2 Proteoglycan-Dependent Contributions of Pericytes and Macrophages to Brain Tumor Vascularization and Progression.Microcirculation. 2016 Feb;23(2):122-33. doi: 10.1111/micc.12251. Microcirculation. 2016. PMID: 26465118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akitaya T, Bronner-Fraser M. Expression of cell adhesion molecules during initiation of and cessation of neural crest cell migration. Dev Dyn. 1992;194:12–20. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama SK, Hasegawa E, Hasegawa T, Yamada KM. The interaction of fibronectin fragments with fibroblastic cells. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:13256–13260. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, Vakaet L, Friis R, Winterhager E, Van Roy F, Mareel MM, Birchmeier W. Loss of epithelial differentiation and gain of invasiveness correlates with tyrosine phosphorylation of the E-cadherin/β-catenin complex in cells transformed with a temperature-sensitive v-SRC gene. J Cell Biol. 1993;120:757–766. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

