Requirements for CD1d recognition by human invariant Valpha24+ CD4-CD8- T cells
- PMID: 9207002
- PMCID: PMC2198960
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.1.109
Requirements for CD1d recognition by human invariant Valpha24+ CD4-CD8- T cells
Abstract
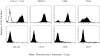
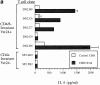
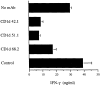
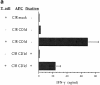
A subset of human CD4-CD8- T cells that expresses an invariant Valpha24-JalphaQ T cell receptor (TCR)-alpha chain, paired predominantly with Vbeta11, has been identified. A series of these Valpha24 Vbeta11 clones were shown to have TCR-beta CDR3 diversity and express the natural killer (NK) locus-encoded C-type lectins NKR-P1A, CD94, and CD69. However, in contrast to NK cells, they did not express killer inhibitory receptors, CD16, CD56, or CD57. All invariant Valpha24(+) clones recognized the MHC class I-like CD16 molecule and discriminated between CD1d and other closely related human CD1 proteins, indicating that recognition was TCR-mediated. Recognition was not dependent upon an endosomal targeting motif in the cytoplasmic tail of CD1d. Upon activation by anti-CD3 or CD1d, the clones produced both Th1 and Th2 cytokines. These results demonstrate that human invariant Valpha24+ CD4-CD8- T cells, and presumably the homologous murine NK1+ T cell population, are CD1d reactive and functionally distinct from NK cells. The conservation of this cell population and of the CD1d ligand across species indicates an important immunological function.
Figures


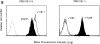
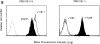


References
-
- Aruffo A, Seed B. Expression of cDNA clones encoding the thymocyte antigens CD1a, b, c demonstrates a hierarchy of exclusion in fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1989;143:1723–1730. - PubMed
-
- Blumberg RS, Gerdes D, Chott A, Porcelli SA, Balk SP. Structure and function of the CD1 family of MHC-like cell surface proteins. Immunol Rev. 1995;147:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Porcelli SA. The CD1 family: a third lineage of antigen-presenting molecules. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:1–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

