A model of excitation and adaptation in bacterial chemotaxis
- PMID: 9207079
- PMCID: PMC23809
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.14.7263
A model of excitation and adaptation in bacterial chemotaxis
Abstract
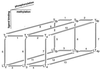
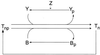
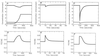
Bacterial chemotaxis is widely studied because of its accessibility and because it incorporates processes that are important in a number of sensory systems: signal transduction, excitation, adaptation, and a change in behavior, all in response to stimuli. Quantitative data on the change in behavior are available for this system, and the major biochemical steps in the signal transduction/processing pathway have been identified. We have incorporated recent biochemical data into a mathematical model that can reproduce many of the major features of the intracellular response, including the change in the level of chemotactic proteins to step and ramp stimuli such as those used in experimental protocols. The interaction of the chemotactic proteins with the motor is not modeled, but we can estimate the degree of cooperativity needed to produce the observed gain under the assumption that the chemotactic proteins interact directly with the motor proteins.
Figures
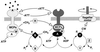
References
-
- Berg H C. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:539–545. - PubMed
-
- Block S M, Segall J E, Berg H C. Cell. 1982;31:215–226. - PubMed
-
- Stock J B. In: Regulation of Cellular Signal Transduction Pathways by Desensitization and Amplification. Sibley D R, Houslay M D, editors. New York: Wiley; 1994. pp. 3–24.
-
- Stock J B, Surette M G. Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology. Washington, DC: Am. Soc. Microbiol.; 1996.
-
- Bourret R B, Borkovich K A, Simon M I. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:401–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

