Myelin basic protein-specific T helper 2 (Th2) cells cause experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in immunodeficient hosts rather than protect them from the disease
- PMID: 9221760
- PMCID: PMC2198987
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.2.307
Myelin basic protein-specific T helper 2 (Th2) cells cause experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in immunodeficient hosts rather than protect them from the disease
Abstract
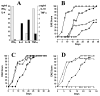
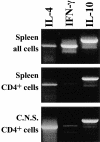
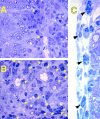
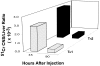
Chronic inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis are caused by CD4(+) Th1 cells. Because Th2 cells antagonize Th1 cell functions in several ways, it is believed that immune deviation towards Th2 can prevent or cure autoimmune diseases. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) is a demyelinating disease used as a model for multiple sclerosis. Using an adoptive transfer system we assessed the role of Th1 and Th2 cells in EAE. In vitro generated Th1 and Th2 cells from myelin basic protein (MBP)-specific TCR transgenic mice were transferred into normal and immunodeficient mice. Th1 cells caused EAE in all recipients after a brief preclinical phase. Surprisingly, Th2 cells also caused EAE in RAG-1 KO mice and in alphabeta T cell-deficient mice, albeit after a longer preclinical phase. Normal or gammadelta T cell-deficient mice were resistant to EAE induced by Th2 cells. The histopathological features of this disease resembled those of an allergic process. In addition, disease induction by Th1 cells was not altered by coadmininstration of Th2 cells in any of the recipients. These findings indicate that MBP-specific Th2 cells have the potential to induce EAE and that the disease induced by previously activated Th1 cells cannot be prevented by normal lymphocytes nor by previously activated Th2 cells.
Figures
References
-
- Mosmann TR, Coffman RL. Th1 and Th2 cells: different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Ann Rev Immunol. 1989;7:145–173. - PubMed
-
- Abbas AK, Murphy KM, Sher A. Functional diversity of helper lymphocytes. Nature (Lond) 1996;383:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh CS, Macatonia SE, Tripp CS, Wolf SF, O'Garra A, Murphy KM. Development of Th1 CD4+T cells through IL-12 produced by Listeria-induced macrophages. Science (Wash DC) 1993;260:547–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

