The evolution of plant nuclear genes
- PMID: 9223265
- PMCID: PMC33705
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.7791
The evolution of plant nuclear genes
Abstract
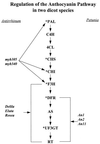
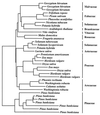
We analyze the evolutionary dynamics of three of the best-studied plant nuclear multigene families. The data analyzed derive from the genes that encode the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (rbcS), the gene family that encodes the enzyme chalcone synthase (Chs), and the gene family that encodes alcohol dehydrogenases (Adh). In addition, we consider the limited evolutionary data available on plant transposable elements. New Chs and rbcS genes appear to be recruited at about 10 times the rate estimated for Adh genes, and this is correlated with a much smaller average gene family size for Adh genes. In addition, duplication and divergence in function appears to be relatively common for Chs genes in flowering plant evolution. Analyses of synonymous nucleotide substitution rates for Adh genes in monocots reject a linear relationship with clock time. Replacement substitution rates vary with time in a complex fashion, which suggests that adaptive evolution has played an important role in driving divergence following gene duplication events. Molecular population genetic studies of Adh and Chs genes reveal high levels of molecular diversity within species. These studies also reveal that inter- and intralocus recombination are important forces in the generation allelic novelties. Moreover, illegitimate recombination events appear to be an important factor in transposable element loss in plants. When we consider the recruitment and loss of new gene copies, the generation of allelic diversity within plant species, and ectopic exchange among transposable elements, we conclude that recombination is a pervasive force at all levels of plant evolution.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular evolution of the chalcone synthase multigene family in the morning glory genome.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jan;42(1):79-92. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10688131 Review.
-
Substitution rate comparisons between grasses and palms: synonymous rate differences at the nuclear gene Adh parallel rate differences at the plastid gene rbcL.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Sep 17;93(19):10274-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.19.10274. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8816790 Free PMC article.
-
A gene duplication/loss event in the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate-carboxylase/oxygenase (rubisco) small subunit gene family among accessions of Arabidopsis thaliana.Mol Biol Evol. 2011 Jun;28(6):1861-76. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr008. Epub 2011 Jan 10. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. PMID: 21220760
-
Molecular phylogeny and evolution of alcohol dehydrogenase (Adh) genes in legumes.BMC Plant Biol. 2005 Apr 18;5:6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-5-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2005. PMID: 15836788 Free PMC article.
-
Transposable element contributions to plant gene and genome evolution.Plant Mol Biol. 2000 Jan;42(1):251-69. Plant Mol Biol. 2000. PMID: 10688140 Review.
Cited by
-
Origin and Reticulate Evolutionary Process of Wheatgrass Elymus trachycaulus (Triticeae: Poaceae).PLoS One. 2015 May 6;10(5):e0125417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125417. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25946188 Free PMC article.
-
Coevolution in Hybrid Genomes: Nuclear-Encoded Rubisco Small Subunits and Their Plastid-Targeting Translocons Accompanying Sequential Allopolyploidy Events in Triticum.Mol Biol Evol. 2020 Dec 16;37(12):3409-3422. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa158. Mol Biol Evol. 2020. PMID: 32602899 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion of the gamma-gliadin gene family in Aegilops and Triticum.BMC Evol Biol. 2012 Nov 8;12:215. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-12-215. BMC Evol Biol. 2012. PMID: 23137212 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis and mapping of gene families encoding beta-1,3-glucanases of soybean.Genetics. 1999 Sep;153(1):445-52. doi: 10.1093/genetics/153.1.445. Genetics. 1999. PMID: 10471725 Free PMC article.
-
Plastid-localized acetyl-CoA carboxylase of bread wheat is encoded by a single gene on each of the three ancestral chromosome sets.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Dec 9;94(25):14179-84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.25.14179. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9391173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Curtis S E, Clegg M T. Mol Biol Evol. 1984;1:291–301. - PubMed
-
- Ritland K, Clegg M T. Am Nat. 1987;130:S74–S100.
-
- Chase M W, Soltis D E, Olmsted R G, Morgan D, Les D H, et al. Ann Missouri Bot Gard. 1993;80:528–580.
-
- Soltis D E, Soltis P S. Evol Biol. 1995;28:139–194.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

