Molecular cloning and functional expression of a human cDNA encoding the antimutator enzyme 8-hydroxyguanine-DNA glycosylase
- PMID: 9223306
- PMCID: PMC21548
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8016
Molecular cloning and functional expression of a human cDNA encoding the antimutator enzyme 8-hydroxyguanine-DNA glycosylase
Abstract
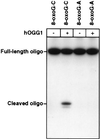
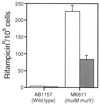
The major mutagenic base lesion in DNA caused by exposure to reactive oxygen species is 8-hydroxyguanine (8-oxo-7, 8-dihydroguanine). In bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, this damaged base is excised by a DNA glycosylase with an associated lyase activity for chain cleavage. We have cloned, sequenced, and expressed a human cDNA with partial sequence homology to the relevant yeast gene. The encoded 47-kDa human enzyme releases free 8-hydroxyguanine from oxidized DNA and introduces a chain break in a double-stranded oligonucleotide specifically at an 8-hydroxyguanine residue base paired with cytosine. Expression of the human protein in a DNA repair-deficient E. coli mutM mutY strain partly suppresses its spontaneous mutator phenotype. The gene encoding the human enzyme maps to chromosome 3p25. These results show that human cells have an enzyme that can initiate base excision repair at mutagenic DNA lesions caused by active oxygen.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterization of hOGG1, a human homolog of the OGG1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Jul 22;94(15):8010-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8010. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9223305 Free PMC article.
-
Excision repair of 8-hydroxyguanine in mammalian cells: the mouse Ogg1 protein as a model.Free Radic Res. 1998 Dec;29(6):487-97. doi: 10.1080/10715769800300541. Free Radic Res. 1998. PMID: 10098454
-
Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the OGG1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which codes for a DNA glycosylase that excises 7,8-dihydro-8-oxoguanine and 2,6-diamino-4-hydroxy-5-N-methylformamidopyrimidine.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 May 28;93(11):5197-202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.11.5197. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8643552 Free PMC article.
-
The OGG1 gene encodes a repair enzyme for oxidatively damaged DNA and is involved in human carcinogenesis.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2001 Aug;3(4):597-609. doi: 10.1089/15230860152542952. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2001. PMID: 11554447 Review.
-
The human OGG1 gene: structure, functions, and its implication in the process of carcinogenesis.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000 May 1;377(1):1-8. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.1773. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. PMID: 10775435 Review.
Cited by
-
Neil3, the final frontier for the DNA glycosylases that recognize oxidative damage.Mutat Res. 2013 Mar-Apr;743-744:4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23274422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissection of the molecular defects caused by pathogenic mutations in the DNA repair factor XPC.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Dec;28(23):7225-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00781-08. Epub 2008 Sep 22. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18809580 Free PMC article.
-
Thermostable repair enzyme for oxidative DNA damage from extremely thermophilic bacterium, Thermus thermophilus HB8.Nucleic Acids Res. 1998 Feb 15;26(4):903-10. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.4.903. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998. PMID: 9461446 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of the glycosylase reaction with hOGG1 base-excision repair enzyme: concerted effect of Lys249 and Asp268 during excision of 8-oxoguanine.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 May 19;45(9):5231-5242. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx157. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28334993 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of two archaeal 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylases provide structural insight into guanine/8-oxoguanine distinction.Structure. 2009 May 13;17(5):703-12. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2009.03.007. Structure. 2009. PMID: 19446526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindahl T. Nature (London) 1993;362:709–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

