Synergistic and promoter-selective activation of transcription by recruitment of transcription factors TFIID and TFIIB
- PMID: 9223310
- PMCID: PMC21552
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.8036
Synergistic and promoter-selective activation of transcription by recruitment of transcription factors TFIID and TFIIB
Abstract
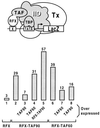
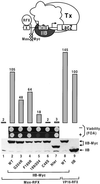
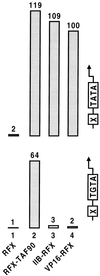
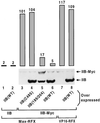
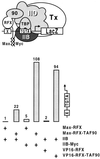
Eukaryotic transcriptional activators may function by stimulating formation of RNA polymerase II preinitiation complexes at the core promoter of genes. In this case, their mode of action will intrinsically depend on how these complexes assemble on promoters in living cells, an issue that remains largely unexplored. Here we show that in yeast the basal transcription machinery is brought to the promoter in the form of at least two subcomplexes, TFIID and a complex comprising TFIIB and other essential components. Individual recruitment of either complex by artificial contact with a transcriptionally inactive, sequence-specific DNA-binding protein suffices to trigger transcriptional activation from a wild-type core promoter bearing the appropriate binding site. In contrast, activation from a promoter containing a weakened TATA element is only observed upon recruitment of TFIID. Tethering TFIIB on that promoter remains without effect, but the simultaneous recruitment of both components leads to strong synergistic activation. These findings suggest a simple mechanism whereby two activators that contact distinct subcomplexes of the basal machinery may stimulate transcription synergistically and differentially depending on the nature of the promoter.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

