Reproducibility and sensitivity of scanning laser Doppler flowmetry during graded changes in PO2
- PMID: 9227199
- PMCID: PMC1722185
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.81.5.360
Reproducibility and sensitivity of scanning laser Doppler flowmetry during graded changes in PO2
Abstract
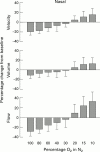
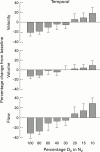
Aims/background: Recently a commercially available scanning laser Doppler flowmeter has been produced, which provides two dimensional maps of the retinal perfusion. The aim of the present study was to investigate the reproducibility and the sensitivity of these measurements.
Methods: 16 healthy subjects were randomised to inhale different gas mixtures of oxygen and nitrogen in a double blind crossover study. The following gas mixtures of oxygen and nitrogen were administered: 100% oxygen + 0% nitrogen, 80% oxygen + 20% nitrogen, 60% oxygen + 40% nitrogen, 40% oxygen + 60% nitrogen, 30% oxygen + 70% nitrogen, 20% oxygen + 80% nitrogen, 15% oxygen + 85% nitrogen, and 10% oxygen + 90% nitrogen. Retinal haemodynamic variables and systemic haemodynamics were measured during all inhalation periods. Recordings under resting conditions were performed three times to calculate intraclass coefficients.
Results: In two subjects we did not obtain technically adequate results. A dose dependent change in retinal blood flow during graded oxygen breathing was observed (p < 0.001). During 100% oxygen breathing blood flow decrease was between 29% and 33%, whereas blood flow increase was between 28% and 33% during inhalation of 10% oxygen + 90% nitrogen.
Conclusions: Scanning laser Doppler flowmetry has an acceptable reproducibility and is appropriate for description of the effect of graded changes in PO2 on retinal haemodynamics. The main problems with the system are the large zero offset, the fixation during retinal scanning, and the neglect of blood flow changes during the cardiac cycle.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
