A novel Rab9 effector required for endosome-to-TGN transport
- PMID: 9230071
- PMCID: PMC2138197
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.2.283
A novel Rab9 effector required for endosome-to-TGN transport
Abstract
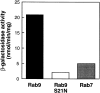
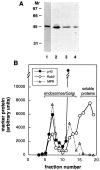
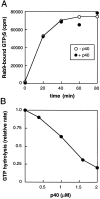
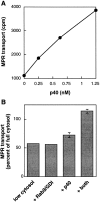
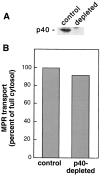
Rab9 GTPase is required for the transport of mannose 6-phosphate receptors from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network in living cells, and in an in vitro system that reconstitutes this process. We have used the yeast two-hybrid system to identify proteins that interact preferentially with the active form of Rab9. We report here the discovery of a 40-kD protein (p40) that binds Rab9-GTP with roughly fourfold preference to Rab9-GDP. p40 does not interact with Rab7 or K-Ras; it also fails to bind Rab9 when it is bound to GDI. The protein is found in cytosol, yet a significant fraction (approximately 30%) is associated with cellular membranes. Upon sucrose density gradient flotation, membrane- associated p40 cofractionates with endosomes containing mannose 6-phosphate receptors and the Rab9 GTPase. p40 is a very potent transport factor in that the pure, recombinant protein can stimulate, significantly, an in vitro transport assay that measures transport of mannose 6-phosphate receptors from endosomes to the trans-Golgi network. The functional importance of p40 is confirmed by the finding that anti-p40 antibodies inhibit in vitro transport. Finally, p40 shows synergy with Rab9 in terms of its ability to stimulate mannose 6-phosphate receptor transport. These data are consistent with a model in which p40 and Rab9 act together to drive the process of transport vesicle docking.
Figures




References
-
- Bork P, Doolittle RF. Drosophila kelchmotif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J Mol Biol. 1994;236:1277–1282. - PubMed
-
- Bucci C, Parton RG, Mather IH, Stunnenberg H, Simons K, Hoflack B, Zerial M. The small GTPase Rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992;70:715–728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

