Molecular tuning of an EF-hand-like calcium binding loop. Contributions of the coordinating side chain at loop position 3
- PMID: 9236210
- PMCID: PMC2233790
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.110.2.173
Molecular tuning of an EF-hand-like calcium binding loop. Contributions of the coordinating side chain at loop position 3
Abstract
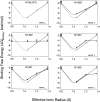
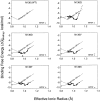
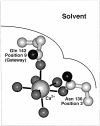
Calcium binding and signaling orchestrate a wide variety of essential cellular functions, many of which employ the EF-hand Ca2+ binding motif. The ion binding parameters of this motif are controlled, in part, by the structure of its Ca2+ binding loop, termed the EF-loop. The EF-loops of different proteins are carefully specialized, or fine-tuned, to yield optimized Ca2+ binding parameters for their unique cellular roles. The present study uses a structurally homologous Ca2+ binding loop, that of the Escherichia coli galactose binding protein, as a model for the EF-loop in studies examining the contribution of the third loop position to intramolecular tuning. 10 different side chains are compared at the third position of the model EF-loop with respect to their effects on protein stability, sugar binding, and metal binding equilibria and kinetics. Substitution of an acidic Asp side chain for the native Asn is found to generate a 6,000-fold increase in the ion selectivity for trivalent over divalent cations, providing strong support for the electrostatic repulsion model of divalent cation charge selectivity. Replacement of Asn by neutral side chains differing in size and shape each alter the ionic size selectivity in a similar manner, supporting a model in which large-ion size selectivity is controlled by complex interactions between multiple side chains rather than by the dimensions of a single coordinating side chain. Finally, the pattern of perturbations generated by side chain substitutions helps to explain the prevalence of Asn and Asp at the third position of natural EF-loops and provides further evidence supporting the unique kinetic tuning role of the gateway side chain at the ninth EF-loop position.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tuning the equilibrium ion affinity and selectivity of the EF-hand calcium binding motif: substitutions at the gateway position.Biochemistry. 1996 May 28;35(21):6697-705. doi: 10.1021/bi952430l. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8639620
-
Kinetic tuning of the EF-hand calcium binding motif: the gateway residue independently adjusts (i) barrier height and (ii) equilibrium.Biochemistry. 1996 Feb 13;35(6):1753-60. doi: 10.1021/bi952335c. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8639655
-
Optimizing the metal binding parameters of an EF-hand-like calcium chelation loop: coordinating side chains play a more important tuning role than chelation loop flexibility.Biochemistry. 1997 Aug 12;36(32):9917-26. doi: 10.1021/bi9703913. Biochemistry. 1997. PMID: 9245425
-
Structural basis for diversity of the EF-hand calcium-binding proteins.J Mol Biol. 2006 Jun 9;359(3):509-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.03.066. Epub 2006 Apr 21. J Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16678204 Review.
-
Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix-loop-helix EF-hand motifs.Biochem J. 2007 Jul 15;405(2):199-221. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070255. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17590154 Review.
Cited by
-
Block of CaV1.2 channels by Gd3+ reveals preopening transitions in the selectivity filter.J Gen Physiol. 2007 Jun;129(6):461-75. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709733. J Gen Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17535959 Free PMC article.
-
How Theoretical Evaluations Can Generate Guidelines for Designing/Engineering Metalloproteins with Desired Metal Affinity and Selectivity.Molecules. 2022 Dec 28;28(1):249. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010249. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Barium ions selectively activate BK channels via the Ca2+-bowl site.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jul 10;109(28):11413-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204444109. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22733762 Free PMC article.
-
Rational design of a novel calcium-binding site adjacent to the ligand-binding site on CD2 increases its CD48 affinity.Protein Sci. 2008 Mar;17(3):439-49. doi: 10.1110/ps.073328208. Protein Sci. 2008. PMID: 18287277 Free PMC article.
-
Protein grabs a ligand by extending anchor residues: molecular simulation for Ca2+ binding to calmodulin loop.Biophys J. 2006 May 1;90(9):3043-51. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.078071. Epub 2006 Feb 10. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16473902 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Babu A, Su H, Ryu Y, Gulati J. Determination of residue specificity in the EF-hand of troponin C for Ca2+coordination, by genetic engineering. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:15469–15474. - PubMed
-
- Bootman MD, Berridge MJ. The elemental principles of calcium signaling. Cell. 1995;83:675–678. - PubMed
-
- Brittain HG, Richardson FS, Martin RB. Terbium emission as a probe of calcium binding sites in proteins. J Am Chem Soc. 1976;98:8255–8260. - PubMed
-
- Carafoli E, Garciamartin E, Guerini D. The plasma-membrane calcium pump: Recent developments and future perspectives. Experientia. 1996;52:1091–1100. - PubMed
-
- Chao SH, Suzuki Y, Zysk JR, Cheung WY. Activation of calmodulin by various meta cations as a function of ionic radius. Mol Pharmacol. 1984;26:75–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

