Phosphorylation at a single site in the rat brain sodium channel is necessary and sufficient for current reduction by protein kinase A
- PMID: 9236220
- PMCID: PMC6568332
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-16-06086.1997
Phosphorylation at a single site in the rat brain sodium channel is necessary and sufficient for current reduction by protein kinase A
Abstract
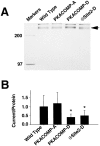
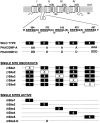
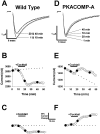
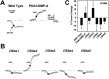
Voltage-gated sodium channels respond to excitatory inputs in nerve cells, generating spikes of depolarization at axon hillock regions and propagating the initial rising phase of action potentials through axons. It previously has been shown that protein kinase A (PKA) attenuates sodium current amplitude 20-50% by phosphorylating serines located in the I-II linker of the sodium channel. We have tested the individual contributions of five PKA consensus sites in the I-II linker by measuring sodium currents expressed in Xenopus oocytes during conditions of PKA induction. PKA was induced by perfusing oocytes with a cocktail that contained forskolin, chlorophenylthio-cAMP, dibutyryl-cAMP, and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine. Phosphorylation at the second PKA site (serine-573) was necessary and sufficient to diminish sodium current amplitude. Phosphorylation at the third and fourth positions (serine-610 and serine-623) reduced current amplitude, but the effect was considerably smaller at those positions. Introduction of a negative charge at site 2 by substitution of serine-573 with an aspartate constitutively reduced the basal level of sodium current, indicating that the attenuation of sodium current by phosphorylation of site 2 by PKA results from the introduction of a negative charge at this site.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phosphorylation of brain sodium channels in the I--II linker modulates channel function in Xenopus oocytes.J Neurosci. 1996 Mar 15;16(6):1965-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-06-01965.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8604040 Free PMC article.
-
cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of the tetrodotoxin-resistant voltage-dependent sodium channel SNS.J Physiol. 1999 Apr 15;516 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):433-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0433v.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10087343 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analysis of the rat I sodium channel in xenopus oocytes.J Neurosci. 1998 Feb 1;18(3):811-20. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-03-00811.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9437003 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular properties of brain sodium channels: an important target for anticonvulsant drugs.Adv Neurol. 1999;79:441-56. Adv Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10514834 Review.
-
Structure, function and expression of voltage-dependent sodium channels.Mol Neurobiol. 1993 Fall-Winter;7(3-4):383-428. doi: 10.1007/BF02769184. Mol Neurobiol. 1993. PMID: 8179845 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel SCN1A mutation associated with generalized epilepsy with febrile seizures plus--and prevalence of variants in patients with epilepsy.Am J Hum Genet. 2001 Apr;68(4):866-73. doi: 10.1086/319524. Epub 2001 Mar 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11254445 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Gated Na+ Channel Isoforms and Their mRNA Expression Levels and Protein Abundance in Three Electric Organs and the Skeletal Muscle of the Electric Eel Electrophorus electricus.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 1;11(12):e0167589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167589. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27907137 Free PMC article.
-
Dopaminergic regulation of neuronal excitability through modulation of Ih in layer V entorhinal cortex.J Neurosci. 2006 Mar 22;26(12):3229-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4333-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16554474 Free PMC article.
-
mTORC1 induces plasma membrane depolarization and promotes preosteoblast senescence by regulating the sodium channel Scn1a.Bone Res. 2022 Mar 8;10(1):25. doi: 10.1038/s41413-022-00204-1. Bone Res. 2022. PMID: 35256591 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of protein kinase A-induced phosphorylation on the gating mechanism of the brain Na+ channel: model fitting to whole-cell current traces.Biophys J. 1999 Jul;77(1):204-16. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(99)76882-7. Biophys J. 1999. PMID: 10388750 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen T-C, Law B, Kondratyuk T, Rossie S. Identification of soluble protein phosphatases that dephosphorylate voltage-sensitive sodium channels in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7750–7756. - PubMed
-
- Costa MR, Catterall WA. Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel in synaptic nerve ending particles. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:8210–8218. - PubMed
-
- Costa MR, Casnellie JE, Catterall WA. Selective phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the sodium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:7918–7921. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
