Resistance to apoptosis caused by PIG-A gene mutations in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
- PMID: 9238050
- PMCID: PMC23114
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.16.8756
Resistance to apoptosis caused by PIG-A gene mutations in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Abstract
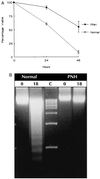
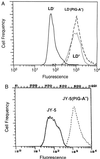
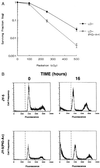
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a clonal hematopoietic stem cell disorder resulting from mutations in an X-linked gene, PIG-A, that encodes an enzyme required for the first step in the biosynthesis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors. PIG-A mutations result in absent or decreased cell surface expression of all GPI-anchored proteins. Although many of the clinical manifestations (e.g., hemolytic anemia) of the disease can be explained by a deficiency of GPI-anchored complement regulatory proteins such as CD59 and CD55, it is unclear why the PNH clone dominates hematopoiesis and why it is prone to evolve into acute leukemia. We found that PIG-A mutations confer a survival advantage by making cells relatively resistant to apoptotic death. When placed in serum-free medium, granulocytes and affected CD34(+) (CD59(-)) cells from PNH patients survived longer than their normal counterparts. PNH cells were also relatively resistant to apoptosis induced by ionizing irradiation. Replacement of the normal PIG-A gene in PNH cell lines reversed the cellular resistance to apoptosis. Inhibited apoptosis resulting from PIG-A mutations appears to be the principle mechanism by which PNH cells maintain a growth advantage over normal progenitors and could play a role in the propensity of this disease to transform into more aggressive hematologic disorders. These data also suggest that GPI anchors are important in regulating apoptosis.
Figures
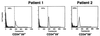

References
-
- Hillmen P, Lewis S M, Bessler M, Luzzatto L, Dacie J V. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1253–1258. - PubMed
-
- Rotoli B, Luzzatto L. Bailliere’s Clin Haematol. 1989;2:113–138. - PubMed
-
- Takeda J, Miyata T, Kawagoe K, Iida Y, Endo Y, Fujita T, Takahashi M, Kitani T, Kinoshita T. Cell. 1993;73:703–711. - PubMed
-
- Miyata T, Yamada N, Iida Y, Nishimura J, Takeda J, Kitani T, Kinoshita T. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:249–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

