Endothelial-dependent mechanisms regulate leukocyte transmigration: a process involving the proteasome and disruption of the vascular endothelial-cadherin complex at endothelial cell-to-cell junctions
- PMID: 9254650
- PMCID: PMC2199034
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.4.517
Endothelial-dependent mechanisms regulate leukocyte transmigration: a process involving the proteasome and disruption of the vascular endothelial-cadherin complex at endothelial cell-to-cell junctions
Abstract
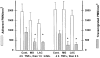
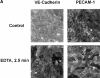
Although several adhesion molecules expressed on leukocytes (beta1 and beta2 integrins, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 [PECAM-1], and CD47) and on endothelium (intercellular adhesion molecule 1, PECAM-1) have been implicated in leukocyte transendothelial migration, less is known about the role of endothelial lateral junctions during this process. We have shown previously (Read, M.A., A.S. Neish, F.W. Luscinskas, V.J. Palambella, T. Maniatis, and T. Collins. 1995. Immunity. 2:493-506) that inhibitors of the proteasome reduce lymphocyte and neutrophil adhesion and transmigration across TNF-alpha-activated human umbilical vein endothelial cell (EC) monolayers in an in vitro flow model. The current study examined EC lateral junction proteins, principally the vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin complex and the effects of proteasome inhibitors (MG132 and lactacystin) on lateral junctions during leukocyte adhesion, to gain a better understanding of the role of EC junctions in leukocyte transmigration. Both biochemical and indirect immunofluorescence analyses of the adherens junction zone of EC monolayers revealed that neutrophil adhesion, not transmigration, induced disruption of the VE-cadherin complex and loss of its lateral junction localization. In contrast, PECAM-1, which is located at lateral junctions and is implicated in neutrophil transmigration, was not altered. These findings identify new and interrelated endothelial-dependent mechanisms for leukocyte transmigration that involve alterations in lateral junction structure and a proteasome-dependent event(s).
Figures









References
-
- Schleimer RP, Rutledge RK. Cultured human vascular endothelial cells acquire adhesiveness for leukocytes following stimulation with interleukin-1, endotoxin and tumor-promoting phorbol-esters. J Immunol. 1986;136:649–656. - PubMed
-
- Read MA, Neish AS, Luscinskas FW, Palombella VJ, Maniatis T, Collins T. The proteasome pathway is required for cytokine-induced endothelial–leukocyte adhesion molecule expression. Immunity. 1995;2:493–506. - PubMed
-
- Dejana E, Corada M, Lampugnani G. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions. FASEB J. 1995;9:910–918. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

