Differential expression of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive neuronal nicotinic receptors in adrenergic chromaffin cells: a role for transcription factor Egr-1
- PMID: 9254668
- PMCID: PMC6573139
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-17-06554.1997
Differential expression of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive neuronal nicotinic receptors in adrenergic chromaffin cells: a role for transcription factor Egr-1
Abstract
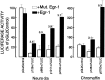
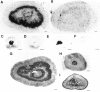
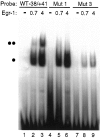
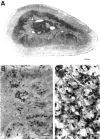
Adrenomedullary chromaffin cells express at least two subtypes of acetylcholine nicotinic receptors, which differ in their sensitivity to the snake toxin alpha-bungarotoxin. One subtype is involved in the activation step of the catecholamine secretion process and is not blocked by the toxin. The other is alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive, and its functional role has not yet been defined. The alpha7 subunit is a component of this subtype. Autoradiography of bovine adrenal gland slices with alpha-bungarotoxin indicates that these receptors are restricted to medullary areas adjacent to the adrenal cortex and colocalize with the enzyme phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase (PNMT), which confers the adrenergic phenotype to chromaffin cells. Transcripts corresponding to the alpha7 subunit also are localized exclusively to adrenergic cells. To identify possible transcriptional regulatory elements of the alpha7 subunit gene involved in the restricted expression of nicotinic receptors, we isolated and characterized its 5' flanking region, revealing putative binding sites for the immediate early gene transcription factor Egr-1, which is known to activate PNMT expression. In reporter gene transfection experiments, Egr-1 increased alpha7 promoter activity by up to sevenfold. Activation was abolished when the most promoter-proximal of the Egr-1 sites was mutated, whereas modification of a close upstream site produced a partial decrease of the Egr-1 response. Because Egr-1 was found to be expressed exclusively in adrenergic cells, we suggest that this transcription factor may be part of a common mechanism involved in the induction of the adrenergic phenotype and the differential expression of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic receptors in the adrenal gland.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Phorbol ester activation of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit gene: involvement of transcription factor Egr-1.J Neurochem. 2000 Mar;74(3):932-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0740932.x. J Neurochem. 2000. PMID: 10693923
-
Glucocorticoid activation of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit gene: involvement of transcription factor Egr-1.FEBS Lett. 2004 May 21;566(1-3):247-50. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2004.04.049. FEBS Lett. 2004. PMID: 15147903
-
Acetylcholine nicotinic receptor subtypes in chromaffin cells.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Jan;470(1):13-20. doi: 10.1007/s00424-017-2050-7. Epub 2017 Aug 8. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 28791474 Review.
-
GC- and E-box motifs as regulatory elements in the proximal promoter region of the neuronal nicotinic receptor alpha7 subunit gene.J Biol Chem. 1998 Aug 7;273(32):20021-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.32.20021. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9685340
-
Neuronal nicotinic alpha-bungarotoxin sites.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;66(8):971-9. doi: 10.1139/y88-160. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1988. PMID: 2846139 Review.
Cited by
-
The novel Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchange inhibitor KB-R7943 also blocks native and expressed neuronal nicotinic receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(8):1893-902. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703519. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10952680 Free PMC article.
-
Functional characterization of alpha9-containing cholinergic nicotinic receptors in the rat adrenal medulla: implication in stress-induced functional plasticity.J Neurosci. 2010 May 12;30(19):6732-42. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4997-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20463235 Free PMC article.
-
α3β4 Acetylcholine Nicotinic Receptors Are Components of the Secretory Machinery Clusters in Chromaffin Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 14;23(16):9101. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169101. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012367 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of the neuronal nicotinic receptor α7 by HIV glycoprotein 120: potential implications for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jan 27;287(5):3079-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.262543. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22084248 Free PMC article.
-
α-Conotoxins Identify the α3β4* Subtype as the Predominant Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Expressed in Human Adrenal Chromaffin Cells.Mol Pharmacol. 2015 Nov;88(5):881-93. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.100982. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Mol Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26330550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alkondon M, Albuquerque E. Diversity of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in rat hippocampal neurons. I. Pharmacological and functional evidence for distinct structural subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1455–1473. - PubMed
-
- Biedler J, Helson L, Spengler B. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973;33:2643–2652. - PubMed
-
- Campos-Caro A, Smillie FI, Domínguez del Toro E, Rovira JC, Vicente-Agulló F, Chapuli J, Juíz JM, Sala S, Sala F, Ballesta JJ, Criado M. Neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on bovine chromaffin cells: cloning, expression, and genomic organization of receptor subunits. J Neurochem. 1997;68:488–497. - PubMed
-
- Ceccatelli S, Dagerlind A, Schalling M, Wikstrom A-C, Okret S, Gustafsson JA, Goldstein M, Hökfelt T. The glucocorticoid receptor in the adrenal gland is localized in the cytoplasm of adrenaline cells. Acta Physiol Scand. 1989;137:559–560. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
