Kappa-opioid receptor activation modulates Ca2+ currents and secretion in isolated neuroendocrine nerve terminals
- PMID: 9254669
- PMCID: PMC6573146
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-17-06565.1997
Kappa-opioid receptor activation modulates Ca2+ currents and secretion in isolated neuroendocrine nerve terminals
Abstract
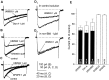
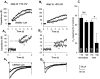
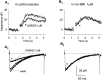
Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were performed together with time-resolved measurements of membrane capacitance (Cm) in nerve terminals acutely dissociated from neurohypophysis of adult rats to investigate modulation of Ca2+ currents and secretion by activation of opioid receptors. Bath superfusion of the kappa-opioid agonists U69,593 (0.3-1 microM), dynorphin A (1 microM), or U50,488H (1-3 microM) reversibly suppressed the peak amplitude of Ca2+ currents 32. 7 +/- 2.7% (in 41 of 56 terminals), 37.4 +/- 5.3% (in 5 of 8 terminals), and 33.5 +/- 8.1% (in 5 of 10 terminals), respectively. In contrast, tests in 11 terminals revealed no effect of the mu-opioid agonist [D-Pen2,5]-enkephalin (1-3 microM; n = 7) or of the delta-agonist Tyr-D-Ala-Gly-N-Me-Phe-Gly-ol (1 microM; n = 4) on Ca2+ currents. Three components of high-threshold current were distinguished on the basis of their sensitivity to blockade by omega-conotoxin GVIA, nicardipine, and omega-conotoxin MVIIC: N-, L-, and P/Q-type current, respectively. Administration of U69,593 inhibited N-type current in these nerve terminals on average 32%, whereas L-type current was reduced 64%, and P/Q-type current was inhibited 28%. Monitoring of changes in Cm in response to brief depolarizing steps revealed that the kappa-opioid-induced reductions in N-, L-, or P/Q-type currents were accompanied by attenuations in two kinetically distinct components of Ca2+-dependent exocytotic release. These data provide strong evidence of a functional linkage between blockade of Ca2+ influx through voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and inhibitory modulation of release by presynaptic opioid receptors in mammalian central nerve endings.
Figures
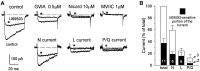


Similar articles
-
Mu-opioid and GABA(B) receptors modulate different types of Ca2+ currents in rat nodose ganglion neurons.Neuroscience. 1998 Aug;85(3):939-56. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00674-x. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9639286
-
Opioid receptor-mediated inhibition of omega-conotoxin GVIA-sensitive calcium channel currents in rat intracardiac neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Feb;79(2):753-62. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.79.2.753. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9463438
-
Mu- and kappa-opioid receptors selectively reduce the same transient components of high-threshold calcium current in rat dorsal root ganglion sensory neurons.J Neurosci. 1994 Oct;14(10):5903-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-10-05903.1994. J Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 7931552 Free PMC article.
-
Optical studies of the secretory event at vertebrate nerve terminals.J Exp Biol. 1988 Sep;139:195-231. doi: 10.1242/jeb.139.1.195. J Exp Biol. 1988. PMID: 2850336 Review.
-
Sodium, calcium and exocytosis: confessions of calcified scientists.J Physiol Paris. 1992;86(1-3):15-21. doi: 10.1016/s0928-4257(05)80003-8. J Physiol Paris. 1992. PMID: 1364194 Review.
Cited by
-
Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jul 8;41:453-473. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-061522. Epub 2018 May 31. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29852083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interplay between the Endogenous Opioid System and Proteasome Complex: Beyond Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 21;20(6):1441. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061441. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30901925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-nociceptive effect of patchouli alcohol: Involving attenuation of cyclooxygenase 2 and modulation of mu-opioid receptor.Chin J Integr Med. 2019 Jun;25(6):454-461. doi: 10.1007/s11655-017-2952-4. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Chin J Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 28795389
-
The molecular neurobiology and neuropathology of opioid use disorder.Curr Res Neurobiol. 2021;2:100023. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2021.100023. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Curr Res Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 35548327 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent opioid-mediated suppression of inhibition between hippocampus and neocortex across species and development.Neuron. 2025 Jun 4;113(11):1805-1822.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2025.03.005. Epub 2025 Mar 26. Neuron. 2025. PMID: 40147437
References
-
- Adamson P, Xiang JZ, Mantzourides T, Brammer MJ, Campbell IC. Presynaptic α2-adrenoceptor and κ-opiate receptor occupancy promotes closure of neuronal (N-type) calcium channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989;174:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Artalejo CR, Adams ME, Fox AP. Three types of Ca2+ channel trigger secretion with different efficacies in chromaffin cells. Nature. 1994;367:72–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
