The mouse pale ear (ep) mutation is the homologue of human Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
- PMID: 9256466
- PMCID: PMC23134
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.17.9238
The mouse pale ear (ep) mutation is the homologue of human Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
Abstract
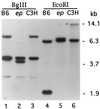
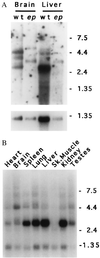
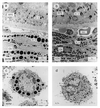
The recessive mutation at the pale ear (ep) locus on mouse chromosome 19 was found to be the homologue of human Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome (HPS). A positional cloning strategy using yeast artificial chromosomes spanning the HPS locus was used to identify the HPS gene and its murine counterpart. These genes and their predicted proteins are highly conserved at the nucleotide and amino acid levels. Sequence analysis of the mutant ep gene revealed the insertion of an intracisternal A particle element in a protein-coding 3' exon. Here we demonstrate that mice with the ep mutation exhibit abnormalities similar to human HPS patients in melanosomes and platelet-dense granules. These results establish an animal model of HPS and will facilitate biochemical and molecular analyses of the functions of this protein in the membranes of specialized intracellular organelles.
Figures


References
-
- Hermansky F, Pudlak P. Blood. 1959;14:162–169. - PubMed
-
- Summers C G, Knobloch W H, Witkop C J, King R A. Ophthalmology. 1988;95:545–554. - PubMed
-
- King R A, Hearing V J, Oetting W S. In: The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, Seventh Edition. Scriver C R, Beaudet A L, Sly W S, Valle D, editors. New York: McGraw–Hill; 1994. pp. 4353–4392.
-
- Bithell T C. In: Wintrobe’s Clinical Hematology. 9th Ed. Lee G R, Bithell T C, Foerster J, Athens J W, Lukens J N, editors. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger; 1993. pp. 1397–1421.
-
- Weiss H J. In: Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. 3rd Ed. Colman R W, Hirsh J, Marder V J, Salzman E W, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1994. pp. 673–684.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

