Null mutation of mCOUP-TFI results in defects in morphogenesis of the glossopharyngeal ganglion, axonal projection, and arborization
- PMID: 9271116
- PMCID: PMC316414
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.15.1925
Null mutation of mCOUP-TFI results in defects in morphogenesis of the glossopharyngeal ganglion, axonal projection, and arborization
Abstract
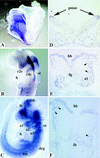
The COUP-TFs are orphan members of the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Multiple COUP-TF members have been cloned and they share a high degree of sequence homology between species as divergent as Drosophila and humans, suggesting a conservation of function through evolution. The COUP-TFs are highly expressed in the developing nervous systems of several species examined, indicating their possible involvement in neuronal development and differentiation. In the mouse, there are two very homologous COUP-TF genes (I and II) and their expression patterns overlap extensively. To study the physiological function of mCOUP-TFI, a gene-targeting approach was undertaken. We report here that mCOUP-TFI null animals die perinataly. Mutant embryos display an altered morphogenesis of the ninth cranial ganglion and nerve. The aberrant formation of the ninth ganglion is most possibly attributable to extra cell death in the neuronal precursor cell population. In addition, at midgestation, aberrant nerve projection and arborization were oberved in several other regions of mutant embryos. These results indicate that mCOUP-TFI is required for proper fetal development and is essential for postnatal development. Furthermore, mCOUP-TFI possesses vital physiological functions that are distinct from mCOUP-TFII despite of their high degree of homology and extensive overlapping expression patterns.
Figures






References
-
- Behringer RR, Crotty DA, Tennyson VM, Brinster RL, Palmiter RD, Wolgemuth DJ. Sequences 5′ of the homeobox of the Hox-1.4 gene direct tissue-specific expression of LacZ during mouse development. Development. 1993;117:823–833. - PubMed
-
- Chazaud CM, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Bouillet P, Decimo D, Chambon P, Dolle P. AP-2.2, a novel gene related to AP-2, is expressed in the forebrain, limbs and face during mouse embryogenesis. Mech Dev. 1996;54:83–94. - PubMed
-
- Cooney A, Tsai S, O’Malley BW, Tsai M-J. Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor (COUP-TF) dimers bind to different GGTCA response elements, allowing COUP-TF to repress hormonal induction of the vitamin D3, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1992;12:4153–4163. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cooney A, Leng X, Tsai S, O’Malley BW, Tsai M-J. Multiple mechanisms of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor-dependent repression of transactivation by the vitamin D, thyroid hormone, and retinoic acid receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:4152–4160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
