PPARgamma induces cell cycle withdrawal: inhibition of E2F/DP DNA-binding activity via down-regulation of PP2A
- PMID: 9271121
- PMCID: PMC316411
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.15.1987
PPARgamma induces cell cycle withdrawal: inhibition of E2F/DP DNA-binding activity via down-regulation of PP2A
Abstract
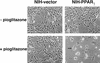
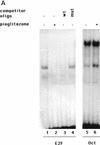
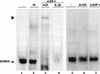
PPAR gamma is an adipose-selective nuclear hormone receptor that plays a key role in the control of adipocyte differentiation. Previous studies indicated that activation of ectopically expressed PPAR gamma induces differentiation when cells have ceased growth because of confluence. We show here that ligand activation of PPAR gamma is sufficient to induce growth arrest in fibroblasts and SV40 large T-antigen transformed, adipogenic HIB1B cells. Cell cycle withdrawal is accompanied by a decrease in the DNA-binding and transcriptional activity of the E2F/DP complex, which is attributable to an increase in the phosphorylation of these proteins, especially DP-1. This effect is a consequence of decreased expression of the catalytic subunit of the serine-threonine phosphatase PP2A. These data suggest an important role for PP2A in the control of E2F/DP activity and a new mode of cell cycle control in differentiation.
Figures





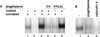

References
-
- Beijersbergen RL, Kerkhoven RM, Zhu L, Carlee L, Mathijs FM, Bernards R. E2F-4, a new member of the E2F gene family, has oncogenic activity and associates with p107 in vivo. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:2680–2690. - PubMed
-
- Brun RP, Tontonoz P, Forman BM, Ellis R, Chen J, Evans RM, Spiegelman BM. Differential activation of adipogenesis by multiple PPAR isoforms. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:974–984. - PubMed
-
- Cao L, Faha B, Dembski M, Tsai LH, Harlow E, Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992;355:176–179. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes & Dev. 1991;5:1538–1552. - PubMed
-
- Chirgwin JM, Przybyla AE, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979;18:5294–5299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
