The lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 I domain is a transient binding module for intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and ICAM-3 in hydrodynamic flow
- PMID: 9271587
- PMCID: PMC2199009
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.5.719
The lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 I domain is a transient binding module for intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and ICAM-3 in hydrodynamic flow
Abstract
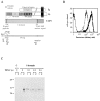
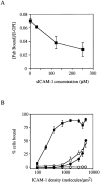
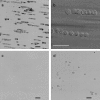
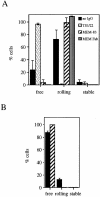
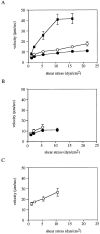
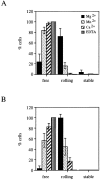
The I domain of lymphocyte function-associated antigen (LFA)-1 contains an intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 and ICAM-3 binding site, but the relationship of this site to regulated adhesion is unknown. To study the adhesive properties of the LFA-1 I domain, we stably expressed a GPI-anchored form of this I domain (I-GPI) on the surface of baby hamster kidney cells. I-GPI cells bound soluble ICAM-1 (sICAM-1) with a low avidity and affinity. Flow cell experiments demonstrated a specific rolling interaction of I-GPI cells on bilayers containing purified full length ICAM-1 or ICAM-3. The LFA-1 activating antibody MEM-83, or its Fab fragment, decreased the rolling velocity of I-GPI cells on ICAM-1-containing membranes. In contrast, the interaction of I-GPI cells with ICAM-3 was blocked by MEM-83. Rolling of I-GPI cells was dependent on the presence of Mg2+. Mn2+ only partially substituted for Mg2+, giving rise to a small fraction of rolling cells and increased rolling velocity. This suggests that the I domain acts as a transient, Mg2+-dependent binding module that cooperates with another Mn2+-stimulated site in LFA-1 to give rise to the stable interaction of intact LFA-1 with ICAM-1.
Figures

References
-
- Dustin ML, Springer TA. Role of lymphocyte adhesion receptors in transient interactions and cell locomotion. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:27–66. - PubMed
-
- Lub M, van Kooyk Y, Figdor CG. Ins and outs of LFA-1. Immunol Today. 1995;16:479–483. - PubMed
-
- Stewart MP, Hogg N. Regulation of leukocyte integrin function: affinity vs. avidity. J Cell Biochem. 1996;61:554–561. - PubMed
-
- Goodman TG, Bajt ML. Identifying the putative metal ion-dependent adhesion site in the β2 (CD18) subunit required for αLβ2 and αMβ2ligand interactions. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:23729–23736. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

