On the reaction mechanism of L-lactate oxidase: quantitative structure-activity analysis of the reaction with para-substituted L-mandelates
- PMID: 9275167
- PMCID: PMC23227
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.18.9590
On the reaction mechanism of L-lactate oxidase: quantitative structure-activity analysis of the reaction with para-substituted L-mandelates
Abstract
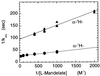
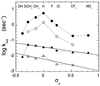
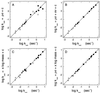
The rate constants for reduction of the flavoenzyme, L-lactate oxidase, and a mutant (in which alanine 95 is replaced by glycine), by a series of para-substituted mandelates, in both the 2-1H- and 2-2H- forms, have been measured by rapid reaction spectrophotometry. In all cases, significant isotope effects (1H/2H = 3-7) on the rate constants of flavin reduction were found, indicating that flavin reduction is a direct measure of alpha-C-H bond breakage. The rate constants show only a small influence of the electronic characteristics of the substituents, but show a good correlation when combined with some substituent volume parameters. A surprisingly good correlation is found with the molecular mass of the substrate. The results are compatible with any mechanism in which there is little development of charge in the transition state. This could be a transfer of hydride to the flavin N(5) position or a synchronous mechanism in which the alpha-C-H is formally abstracted as a H+ while the resulting charge is simultaneously neutralized by another event.
Figures

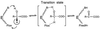
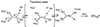
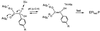
References
-
- Ghisla S, Massey V. In: Chemistry and Biochemistry of Flavoenzymes. Müller F, editor. Vol. 2. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1991. pp. 243–289.
-
- Lederer F. In: Chemistry and Biochemistry of Flavoenzymes. Müller F, editor. Vol. 2. Boca Raton, FL: CRC; 1991. pp. 153–242.
-
- Lindqvist Y, Branden C I, Mathews F S, Lederer F. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:3198–3207. - PubMed
-
- Xia Z X, Mathews F S. J Mol Biol. 1990;212:837–863. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

