Serotonergic inhibition of the T-type and high voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in the primary sensory neurons of Xenopus larvae
- PMID: 9278519
- PMCID: PMC6573265
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-18-06839.1997
Serotonergic inhibition of the T-type and high voltage-activated Ca2+ currents in the primary sensory neurons of Xenopus larvae
Abstract
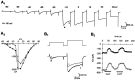
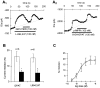
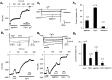
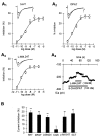
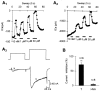
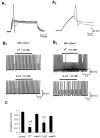
The primary sensory Rohon-Beard (R-B) neurons of Xenopus larvae are highly analogous to the C fibers of the mammalian pain pathway. We explored the actions of 5-HT by studying the modulation of Ca2+ currents. In approximately 80% of the acutely isolated R-B neurons, 5-HT inhibited the high voltage-activated (HVA) currents by 16% (n = 29) and the T-type currents by 24% (n = 41). The modulation of the T-type and the HVA currents was mimicked by selective 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D agonists: 8-OH-DPAT and L-694,247. The effects of the agonists were blocked by their respective 5-HT1A or 5-HT1D antagonists: p-MPPI and GR127935, suggesting that both 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors were involved. Approximately 70% of the actions of 5-HT on HVA currents was occluded by omega-conotoxin-GVIA (N-type channel blocker), whereas the rest of the modulation ( approximately 30%) was occluded by <100 nM omega-agatoxin-TK (P/Q-type channel blocker). This suggests that 5-HT acts on N- and P/Q-type Ca2+ channels. Neither the modulation of the T-type nor that of the HVA currents was accompanied by changes in their voltage-dependent kinetics. Cell-attached patch-clamp recordings suggest that the modulation of the T-type channel occurs through a membrane-delimited second messenger. We have studied the functional consequences of the modulation of T-type Ca2+ channels and have found that these channels play a role in spike initiation in R-B neurons. Modulation of T-type channels by 5-HT therefore could modulate the sensitivity of this sensory pathway by increasing the thresholds of R-B neurons. This is a new and potentially important locus for modulation of sensory pathways in vertebrates.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential inhibition of N and P/Q Ca2+ currents by 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors in spinal neurons of Xenopus larvae.J Physiol. 1998 Jul 1;510 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):103-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.103bz.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9625870 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of voltage-dependent calcium currents by serotonin in acutely isolated rat amygdala neurons.Synapse. 2001 Sep 15;41(4):351-9. doi: 10.1002/syn.1092. Synapse. 2001. PMID: 11494406
-
Effects of serotonin on caudal raphe neurons: inhibition of N- and P/Q-type calcium channels and the afterhyperpolarization.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Mar;77(3):1362-74. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.3.1362. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9084603
-
Inhibition of N- and P-type calcium currents and the after-hyperpolarization in rat motoneurones by serotonin.J Physiol. 1995 Jun 15;485 ( Pt 3)(Pt 3):635-47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020758. J Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7562606 Free PMC article.
-
G-proteins are involved in 5-HT receptor-mediated modulation of N- and P/Q- but not T-type Ca2+ channels.J Neurosci. 1999 Feb 1;19(3):890-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-03-00890.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 9920652 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Buspirone-induced antinociception is mediated by L-type calcium channels and calcium/caffeine-sensitive pools in mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003 Mar;166(3):276-83. doi: 10.1007/s00213-002-1327-4. Epub 2003 Jan 28. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2003. PMID: 12552360
-
Somatostatin inhibits thalamic network oscillations in vitro: actions on the GABAergic neurons of the reticular nucleus.J Neurosci. 2002 Jul 1;22(13):5374-86. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-13-05374.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12097489 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonin suppresses subthreshold and suprathreshold oscillatory activity of rat inferior olivary neurones in vitro.J Physiol. 2000 May 1;524 Pt 3(Pt 3):833-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00833.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10790162 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel-induced epithelial damage and ectopic MMP-13 expression promotes neurotoxicity in zebrafish.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 12;113(15):E2189-98. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525096113. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27035978 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory peptidergic modulation of C. elegans serotonin neurons is gated by T-type calcium channels.Elife. 2017 Feb 6;6:e22771. doi: 10.7554/eLife.22771. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28165324 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Awouters F. The pharmacology of ketanserin, the first selective serotonin S2-antagonist. Drug Dev Res. 1985;6:263–300.
-
- Beer MS, Stanton JA, Bevan Y, Chauhan NS, Middlemiss DN. An investigation of the 5-HT1D receptor binding affinity of 5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-carboxyamidotryptamine, and sumatriptan in the central nervous system of seven species. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992;213:193–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
