Mice lacking the ski proto-oncogene have defects in neurulation, craniofacial, patterning, and skeletal muscle development
- PMID: 9284043
- PMCID: PMC316447
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.16.2029
Mice lacking the ski proto-oncogene have defects in neurulation, craniofacial, patterning, and skeletal muscle development
Abstract
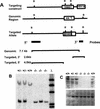
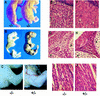
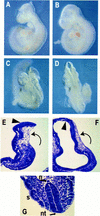
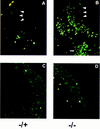
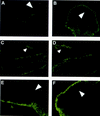
The c-ski proto-oncogene has been implicated in the control of cell growth and skeletal muscle differentiation. To determine its normal functions in vivo, we have disrupted the mouse c-ski gene. Our results show a novel role for ski in the morphogenesis of craniofacial structures and the central nervous system, and confirm its proposed function as a player in skeletal muscle development. Homozygous mutant mice show perinatal lethality resulting from exencephaly, a defect caused by failed closure of the cranial neural tube during neurulation. The timing of the neural tube defect in ski -/- embryos coincides with excessive apoptosis in the cranial neuroepithelium, as well as in the cranial mesenchyme. Homozygous ski mutants also exhibit a dramatic reduction in skeletal muscle mass, consistent with a defect in expansion of a myogenic precursor population. Nestin is an intermediate filament expressed in highly proliferative neuroepithelial stem cells and in myogenic precursors. Interestingly, we find decreased nestin expression in both the cranial neural tube and the somites of ski -/- embryos, compared with their normal littermates, but no reduction of nestin in the caudal neural tube. These results are consistent with a model in which ski activities are required for the successful expansion of a subset of precursors in the neuroepithelial or skeletal muscle lineages.
Figures
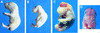
References
-
- Chen ZF, Behringer RR. Twist is required in head mesenchyme cranial neural tube morphogenesis. Genes & Dev. 1995;9:686–699. - PubMed
-
- Colmenares C, Stavnezer E. The ski oncogene induces muscle differentiation in quail embryo cells. Cell. 1989;59:293–303. - PubMed
-
- Copp AJ. Neural tube defects. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:381–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
