Impaired CD28-mediated interleukin 2 production and proliferation in stress kinase SAPK/ERK1 kinase (SEK1)/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4)-deficient T lymphocytes
- PMID: 9294148
- PMCID: PMC2199046
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.6.941
Impaired CD28-mediated interleukin 2 production and proliferation in stress kinase SAPK/ERK1 kinase (SEK1)/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4)-deficient T lymphocytes
Abstract
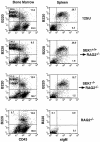
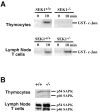
The dual specific kinase SAPK/ERK1 kinase (SEK1; mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4/Jun NH2 terminal kinase [ JNK] kinase) is a direct activator of stress-activated protein kinases ([SAPKs]/JNKs) in response to CD28 costimulation, CD40 signaling, or activation of the germinal center kinase. Here we show that SEK1(-/-) recombination-activating gene (RAG)2(-/-) chimeric mice have a partial block in B cell maturation. However, peripheral B cells displayed normal responses to IL-4, IgM, and CD40 cross-linking. SEK1(-/-) peripheral T cells showed decreased proliferation and IL-2 production after CD28 costimulation and PMA/Ca2+ ionophore activation. Although CD28 expression was absolutely crucial to generate vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-specific germinal centers, SEK1(-/-)RAG2(-/-) chimeras mounted a protective antiviral B cell response, exhibited normal IgG class switching, and made germinal centers in response to VSV. Interestingly, PMA/Ca2+ ionophore stimulation, which mimics TCR-CD3 and CD28-mediated signal transduction, induced SAPK/JNK activation in peripheral T cells, but not in thymocytes, from SEK1(-/-) mice. These results show that signaling pathways for SAPK activation are developmentally regulated in T cells. Although SEK1(-/-) thymocytes failed to induce SAPK/JNK in response to PMA/Ca2+ ionophore, SEK1(-/-)RAG2(-/-) thymocytes proliferated and made IL-2 after PMA/Ca2+ ionophore and CD3/CD28 stimulation, albeit at significantly lower levels compared to SEK1(+/+)RAG2(-/-) thymocytes, implying that CD28 costimulation and PMA/Ca2+ ionophore-triggered signaling pathways exist that can mediate proliferation and IL-2 production independently of SAPK activation. Our data provide the first genetic evidence that SEK1 is an important effector molecule that relays CD28 signaling to IL-2 production and T cell proliferation.
Figures

















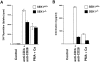
Similar articles
-
Stress-signalling kinase Sek1 protects thymocytes from apoptosis mediated by CD95 and CD3.Nature. 1997 Jan 23;385(6614):350-3. doi: 10.1038/385350a0. Nature. 1997. PMID: 9002521
-
SEK1/MKK4 is required for maintenance of a normal peripheral lymphoid compartment but not for lymphocyte development.Immunity. 1998 May;8(5):625-34. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80567-1. Immunity. 1998. PMID: 9620683
-
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates signal integration of TCR/CD28 costimulation in primary murine T cells.J Immunol. 1999 Apr 1;162(7):3819-29. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10201899
-
Effector pathways regulating T cell activation.Biochem Pharmacol. 1998 Dec 15;56(12):1539-47. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(98)00213-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9973174 Review.
-
Signaling by the JNK group of MAP kinases. c-jun N-terminal Kinase.J Clin Immunol. 2001 Jul;21(4):253-7. doi: 10.1023/a:1010975124110. J Clin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11506194 Review.
Cited by
-
The stress kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MKK)7 is a negative regulator of antigen receptor and growth factor receptor-induced proliferation in hematopoietic cells.J Exp Med. 2001 Sep 17;194(6):757-68. doi: 10.1084/jem.194.6.757. J Exp Med. 2001. PMID: 11560992 Free PMC article.
-
The MKK7 gene encodes a group of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase kinases.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Feb;19(2):1569-81. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.2.1569. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 9891090 Free PMC article.
-
A role for the Tec family kinase ITK in regulating SEB-induced interleukin-2 production in vivo via c-jun phosphorylation.BMC Immunol. 2005 Jul 22;6:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-6-19. BMC Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16042784 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-92a negatively regulates Toll-like receptor (TLR)-triggered inflammatory response in macrophages by targeting MKK4 kinase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Mar 15;288(11):7956-7967. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.445429. Epub 2013 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23355465 Free PMC article.
-
PKCtheta signals activation versus tolerance in vivo.J Exp Med. 2004 Mar 15;199(6):743-52. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031022. J Exp Med. 2004. PMID: 15024044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sturgill TW, Ray LB, Erikson E, Maller JL. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature (Lond) 1988;334:715–718. - PubMed
-
- Boulton TG, Nye SH, Robbins DJ, Ip NY, Radziejewska E, Morgenbesser SD, DePinho RA, Panayotatos N, Cobb MH, Yancopoulos GD. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell. 1991;65:663–675. - PubMed
-
- Ahn NG, Seger R, Bratlien RL, Diltz CD, Tonks NK, Krebs EG. Multiple components in an epidermal growth factor–stimulated protein kinase cascade. In vitro activation of a myelin basic protein/microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4220–4227. - PubMed
-
- Cowley S, Paterson H, Kemp P, Marshall CJ. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1994;77:841–852. - PubMed
-
- Treisman R. Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996;8:205–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

