A study of the interferon antiviral mechanism: apoptosis activation by the 2-5A system
- PMID: 9294150
- PMCID: PMC2199051
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.6.967
A study of the interferon antiviral mechanism: apoptosis activation by the 2-5A system
Abstract
The 2-5A system contributes to the antiviral effect of interferons through the synthesis of 2-5A and its activation of the ribonuclease, RNase L. RNase L degrades viral and cellular RNA after activation by unique, 2'-5' phosphodiester-linked, oligoadenylates [2-5A, (pp)p5' A2'(P5'A2')]n, n >=2. Because both the 2-5A system and apoptosis can serve as viral defense mechanisms and RNA degradation occurs during both processes, we investigated the potential role of RNase L in apoptosis. Overexpression of human RNase L by an inducible promoter in NIH3T3 fibroblasts decreased cell viability and triggered apoptosis. Activation of endogenous RNase L, specifically with 2-5A or with dsRNA, induced apoptosis. Inhibition of RNase L with a dominant negative mutant suppressed poly (I).poly (C)-induced apoptosis in interferon-primed fibroblasts. Moreover, inhibition of RNase L suppressed apoptosis induced by poliovirus. Thus, increased RNase L levels induced apoptosis and inhibition of RNase L activity blocked viral-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis may be one of the antiviral mechanisms regulated by the 2-5A system.
Figures
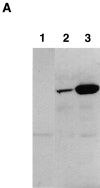

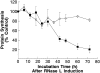


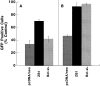
References
-
- Clouston WM, Kerr JFR. Apoptosis, lymphotoxicity and the containment of viral infections. Med Hypotheses. 1985;18:399–404. - PubMed
-
- Clem RJ, Fechheimer M, Miller LK. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science (Wash DC) 1991;254:1388–1390. - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen H, Czarniecki CW, Krause D, Friedman RM, Silverman RH. Interferon-induced synthseis of 2-5A-dependent RNase in mouse JLS-V9R cells. Virology. 1983;125:496–501. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

