The mouse histone H2a gene contains a small element that facilitates cytoplasmic accumulation of intronless gene transcripts and of unspliced HIV-1-related mRNAs
- PMID: 9294170
- PMCID: PMC23318
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10104
The mouse histone H2a gene contains a small element that facilitates cytoplasmic accumulation of intronless gene transcripts and of unspliced HIV-1-related mRNAs
Abstract
Histone mRNAs are naturally intronless and accumulate efficiently in the cytoplasm. To learn whether there are cis-acting sequences within histone genes that allow efficient cytoplasmic accumulation of RNAs, we made recombinant constructs in which sequences from the mouse H2a gene were cloned into a human beta-globin cDNA. By using transient transfection and RNase protection analysis, we demonstrate here that a 100-bp sequence within the H2a coding region permits efficient cytoplasmic accumulation of the globin cDNA transcripts. We also show that this sequence appears to suppress splicing and can functionally replace Rev and the Rev-responsive element in the cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced HIV-1-related mRNAs. Like the Rev-responsive element, this sequence acts in an orientation-dependent manner. We thus propose that the sequence identified here may be a member of the cis-acting elements that facilitate the cytoplasmic accumulation of naturally intronless gene transcripts.
Figures
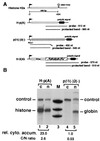
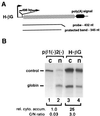
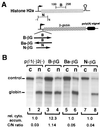
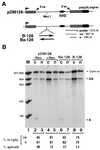
Similar articles
-
Synergistic stimulation of HIV-1 rev-dependent export of unspliced mRNA to the cytoplasm by hnRNP A1.J Mol Biol. 1999 Feb 5;285(5):1951-64. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.2473. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 9925777
-
Intronless mRNA transport elements may affect multiple steps of pre-mRNA processing.EMBO J. 1999 Mar 15;18(6):1642-52. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.6.1642. EMBO J. 1999. PMID: 10075934 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-mRNA processing enhancer (PPE) elements from intronless genes play additional roles in mRNA biogenesis than do ones from intron-containing genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Apr 20;33(7):2215-26. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki506. Print 2005. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005. PMID: 15843684 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the hepatitis B virus posttranscriptional regulatory element in export of intronless transcripts.Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3864-9. doi: 10.1128/MCB.15.7.3864. Mol Cell Biol. 1995. PMID: 7791793 Free PMC article.
-
The strength of the HIV-1 3' splice sites affects Rev function.Retrovirology. 2006 Dec 4;3:89. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-3-89. Retrovirology. 2006. PMID: 17144911 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Splicing is required for rapid and efficient mRNA export in metazoans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Dec 21;96(26):14937-42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.14937. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10611316 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of SLBP results in nuclear retention of histone mRNA.RNA. 2009 Mar;15(3):459-72. doi: 10.1261/rna.1205409. Epub 2009 Jan 20. RNA. 2009. PMID: 19155325 Free PMC article.
-
A new RNA element located in the coding region of a murine endogenous retrovirus can functionally replace the Rev/Rev-responsive element system in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag expression.J Virol. 2001 Nov;75(22):10670-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10670-10682.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11602709 Free PMC article.
-
Viral regulation of mRNA export.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4389-96. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4389-4396.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078920 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The presence of multiple introns is essential for ERECTA expression in Arabidopsis.RNA. 2011 Oct;17(10):1907-21. doi: 10.1261/rna.2825811. Epub 2011 Aug 31. RNA. 2011. PMID: 21880780 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

