The alpha chain of laminin-1 is independently secreted and drives secretion of its beta- and gamma-chain partners
- PMID: 9294185
- PMCID: PMC23337
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10189
The alpha chain of laminin-1 is independently secreted and drives secretion of its beta- and gamma-chain partners
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998 Feb 17;95(4):1968
Abstract
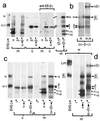
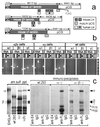
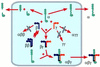
A mammalian recombinant strategy was established to dissect rules of basement membrane laminin assembly and secretion. The alpha-, beta-, and gamma-chain subunits of laminin-1 were expressed in all combinations, transiently and/or stably, in a near-null background. In the absence of its normal partners, the alpha chain was secreted as intact protein and protein that had been cleaved in the coiled-coil domain. In contrast, the beta and gamma chains, expressed separately or together, remained intracellular with formation of betabeta or betagamma, but not gammagamma, disulfide-linked dimers. Secretion of the beta and gamma chains required simultaneous expression of all three chains and their assembly into alphabetagamma heterotrimers. Epitope-tagged recombinant alpha subunit and recombinant laminin were affinity-purified from the conditioned medium of alphagamma and alphabetagamma clones. Rotary-shadow electron microscopy revealed that the free alpha subunit is a linear structure containing N-terminal and included globules with a foreshortened long arm, while the trimeric species has the typical four-arm morphology of native laminin. We conclude that the alpha chain can be delivered to the extracellular environment as a single subunit, whereas the beta and gamma chains cannot, and that the alpha chain drives the secretion of the trimeric molecule. Such an alpha-chain-dependent mechanism could allow for the regulation of laminin export into a nascent basement membrane, and might serve an important role in controlling basement membrane formation.
Figures


References
-
- Yurchenco P D. In: Extracellular Matrix Assembly and Structure. Yurchenco D P, Birk D, Mecham R, editors. New York: Academic; 1994. pp. 351–388.
-
- Timpl R, Brown J C. BioEssays. 1996;18:123–132. - PubMed
-
- Engvall E, Wewer U M. J Cell Biochem. 1996;61:493–501. - PubMed
-
- Burgeson R E, Chiquet M, Deutzmann R, Ekblom P, Engel J, Kleinman H, Martin G R, Meneguzzi G, Paulsson M, Sanes J, Timpl R, Tryggvason K, Yamada Y, Yurchenco P D. Matrix Biol. 1994;14:209–211. - PubMed
-
- Beck K, Hunter I, Engel J. FASEB J. 1990;4:148–160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

