The product of ORF O located within the domain of herpes simplex virus 1 genome transcribed during latent infection binds to and inhibits in vitro binding of infected cell protein 4 to its cognate DNA site
- PMID: 9294219
- PMCID: PMC23371
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.19.10379
The product of ORF O located within the domain of herpes simplex virus 1 genome transcribed during latent infection binds to and inhibits in vitro binding of infected cell protein 4 to its cognate DNA site
Abstract
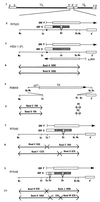
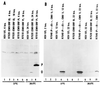
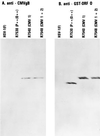
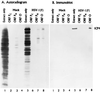
The partially overlapping ORF P and ORF O are located within the domains of the herpes simplex virus 1 genome transcribed during latency. Earlier studies have shown that ORF P is repressed by infected cell protein 4 (ICP4), the major viral regulatory protein, binding to its cognate site at the transcription initiation site of ORF P. The ORF P protein binds to p32, a component of the ASF/SF2 alternate splicing factors; in cells infected with a recombinant virus in which ORF P was derepressed there was a significant decrease in the expression of products of key regulatory genes containing introns. We report that (i) the expression of ORF O is repressed during productive infection by the same mechanism as that determining the expression of ORF P; (ii) in cells infected at the nonpermissive temperature for ICP4, ORF O protein is made in significantly lower amounts than the ORF P protein; (iii) the results of insertion of a sequence encoding 20 amino acids between the putative initiator methionine codons of ORF O and ORF P suggest that ORF O initiates at the methionine codon of ORF P and that the synthesis of ORF O results from frameshift or editing of its RNA; and (iv) glutathione S-transferase-ORF O fusion protein bound specifically ICP4 and precluded its binding to its cognate site on DNA in vitro. These and earlier results indicate that ORF P and ORF O together have the capacity to reduce the synthesis or block the expression of regulatory proteins essential for viral replication in productive infection.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Early expression of herpes simplex virus (HSV) proteins and reactivation of latent infection.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2000;45(1):7-28. doi: 10.1007/BF02817445. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2000. PMID: 11200675 Review.
-
A virus with a mutation in the ICP4-binding site in the L/ST promoter of herpes simplex virus type 1, but not a virus with a mutation in open reading frame P, exhibits cell-type-specific expression of gamma(1)34.5 transcripts and latency-associated transcripts.J Virol. 1998 May;72(5):4250-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.72.5.4250-4264.1998. J Virol. 1998. PMID: 9557715 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 open reading frames O and P are not necessary for establishment of latent infection in mice.J Virol. 2000 Oct;74(19):9019-27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.19.9019-9027.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 10982346 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription of the derepressed open reading frame P of herpes simplex virus 1 precludes the expression of the antisense gamma(1)34.5 gene and may account for the attenuation of the mutant virus.J Virol. 1997 Oct;71(10):7750-7. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.10.7750-7757.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9311860 Free PMC article.
-
HSV gene functions: what have we learned that could be generally applicable to its near and distant cousins?Acta Virol. 1999 Apr-Jun;43(2-3):75-80. Acta Virol. 1999. PMID: 10696424 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective degradation of mRNAs by the HSV host shutoff RNase is regulated by the UL47 tegument protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 30;110(18):E1669-75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1305475110. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23589852 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Small Noncoding RNAs 1 and 2 Activate the Herpesvirus Entry Mediator Promoter.J Virol. 2022 Feb 9;96(3):e0198521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01985-21. Epub 2021 Dec 1. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34851143 Free PMC article.
-
Early expression of herpes simplex virus (HSV) proteins and reactivation of latent infection.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2000;45(1):7-28. doi: 10.1007/BF02817445. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2000. PMID: 11200675 Review.
-
Complete sequence and comparative analysis of the genome of herpes B virus (Cercopithecine herpesvirus 1) from a rhesus monkey.J Virol. 2003 Jun;77(11):6167-77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.11.6167-6177.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12743273 Free PMC article.
-
The miRNAs of herpes simplex virus (HSV).Virol Sin. 2012 Dec;27(6):333-8. doi: 10.1007/s12250-012-3266-5. Epub 2012 Nov 9. Virol Sin. 2012. PMID: 23180288 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roizman B, Sears A E. In: Fields’ Virology. 3rd Ed. Fields B N, Knipe D M, Howley P, Chanock R M, Hirsch M S, Melnick J L, Monath T P, Roizman B, editors. New York: Lipcincott–Raven; 1996. pp. 2231–2295.
-
- Mitchell W J, Lirette R P, Fraser N. J Gen Virol. 1990;71:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Stevens J G, Wagner E K, Devi-Rao G B, Cook M L, Feldman L T. Science. 1987;235:1056–1059. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

