Leukemia inhibitory factor-dependent transcriptional activation in embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 9298977
- PMCID: PMC2132559
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.6.1207
Leukemia inhibitory factor-dependent transcriptional activation in embryonic stem cells
Abstract
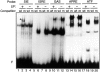
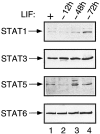
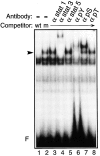
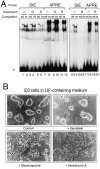
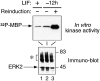
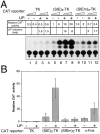
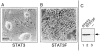
STAT transcription factors are induced by a number of growth factors and cytokines. Within minutes of induction, the STAT proteins are phosphorylated on tyrosine and serine residues and translocated to the nucleus, where they bind to their DNA targets. The leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) mediates pleiotropic and sometimes opposite effects both in vivo and in cultured cells. It is known, for example, to prevent differentiation of embryonic stem (ES) cells in vitro. To get insights into LIF-regulated signaling in ES cells, we have analyzed protein-binding and transcriptional properties of STAT recognition sites in ES cells cultivated in the presence and in the absence of LIF. We have detected a specific LIF-regulated DNA-binding activity implicating the STAT3 protein. We show that STAT3 phosphorylation is essential for this LIF-dependent DNA-binding activity. The possibility that ERK2 or a closely related protein kinase, whose activity is modulated in a LIF-dependent manner, contributes to this phosphorylation is discussed. Finally, we show that the multimerized STAT3-binding DNA element confers LIF responsiveness to a minimal thymidine kinase promoter. This, together with our observation that overexpression of STAT3 dominant-negative mutants abrogates this LIF responsiveness, clearly indicates that STAT3 is involved in LIF-regulated transcriptional events in ES cells. Finally, stable expression of such a dominant negative mutant of STAT3 induces morphological differentiation of ES cells despite continuous LIF supply. Our results suggest that STAT3 is a critical target of the LIF signaling pathway, which maintains pluripotent cell proliferation.
Figures



References
-
- Akira S, Nishio Y, Inoue M, Wang XJ, Wei S, Matsusaka T, Yoshida K, Sudo T, Naruto M, Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning of APRF, a novel IFN-stimulated gene factor 3 p91-related transcription factor involved in the gp130-mediated signaling pathway. Cell. 1994;77:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama T, Ishida J, Nakagawa S, Ogawara H, Watanabe S, Itoh N, Shibuya M, Fukami Y. Genistein, a specific inhibitor of tyrosine-specific protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:5592–5595. - PubMed
-
- Boschart M, Kluppel M, Schmidt A, Schutz G, Luckow B. Reporter constructs with low background activity utilizing the CATgene. Gene (Amst) 1992;110:129–130. - PubMed
-
- Boulter CA, Agguzi A, Williams RL, Wagner EF, Evans MJ, Beddington R. Expression of v-src induces aberrant development and twinning in chimaeric mice. Development (Camb) 1991;111:357–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

