The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and phospholipase D in adaptor recruitment
- PMID: 9298980
- PMCID: PMC2132562
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.138.6.1239
The role of ADP-ribosylation factor and phospholipase D in adaptor recruitment
Abstract
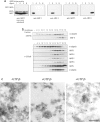
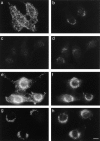
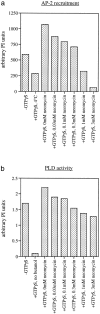
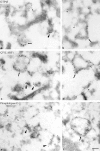
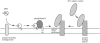
AP-1 and AP-2 adaptors are recruited onto the TGN and plasma membrane, respectively. GTPgammaS stimulates the recruitment of AP-1 onto the TGN but causes AP-2 to bind to an endosomal compartment (Seaman, M.N.J., C.L. Ball, and M.S. Robinson. 1993. J. Cell Biol. 123:1093-1105). We have used subcellular fractionation followed by Western blotting, as well as immunofluorescence and immunogold electron microscopy, to investigate both the recruitment of AP-2 adaptors onto the plasma membrane and their targeting to endosomes, and we have also examined the recruitment of AP-1 under the same conditions. Two lines of evidence indicate that the GTPgammaS-induced targeting of AP-2 to endosomes is mediated by ADP-ribosylation factor-1 (ARF1). First, GTPgammaS loses its effect when added to ARF-depleted cytosol, but this effect is restored by the addition of recombinant myristoylated ARF1. Second, adding constitutively active Q71L ARF1 to the cytosol has the same effect as adding GTPgammaS. The endosomal membranes that recruit AP-2 adaptors have little ARF1 or any of the other ARFs associated with them, suggesting that ARF may be acting catalytically. The ARFs have been shown to activate phospholipase D (PLD), and we find that addition of exogenous PLD has the same effect as GTPgammaS or Q71L ARF1. Neomycin, which inhibits endogenous PLD by binding to its cofactor phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, prevents the recruitment of AP-2 not only onto endosomes but also onto the plasma membrane, suggesting that both events are mediated by PLD. Surprisingly, however, neither PLD nor neomycin has any effect on the recruitment of AP-1 adaptors onto the TGN, even though AP-1 recruitment is ARF mediated. These results indicate that different mechanisms are used for the recruitment of AP-1 and AP-2.
Figures

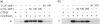
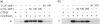




References
-
- Ball CL, Hunt SP, Robinson MS. Expression and localisation of α-adaptin isoforms. J Cell Sci. 1995;108:2865–2875. - PubMed
-
- Barlowe C, Orci L, Yeung T, Hosobuchi M, Hamamoto S, Salama N, Rexach MF, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Schekman R. COPII: a membrane coat formed by sec proteins that drive vesicle budding from the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1994;77:895–907. - PubMed
-
- Beck KA, Keen JH. Interaction of phosphoinositide cycle intermediates with the plasma membrane-associated clathrin assembly protein AP-2. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:4442–4447. - PubMed
-
- Bi K, Roth MG, Ktistakis NT. Phosphatidic acid formation by phospholipase D is required for transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Curr Biol. 1997;7:301–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

