Oral budesonide is as effective as oral prednisolone in active Crohn's disease. The Global Budesonide Study Group
- PMID: 9301500
- PMCID: PMC1891473
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.41.2.209
Oral budesonide is as effective as oral prednisolone in active Crohn's disease. The Global Budesonide Study Group
Abstract
Background: The use of corticosteroids in active Crohn's disease often becomes limited by side effects. Budesonide is a potent corticosteroid with low systemic bioavailability due to an extensive first pass liver metabolism.
Aims: To compare the efficacy and safety of two dosage regimens of budesonide and prednisolone in patients with active Crohn's disease affecting the ileum and/or the ascending colon.
Patients and methods: One hundred and seventy eight patients were randomised to receive budesonide controlled ileal release (CIR) capsules 9 mg once daily or 4.5 mg twice daily, or prednisolone tablets 40 mg once daily. The treatment period was 12 weeks. The primary efficacy variable was clinical remission, defined as a Crohn's Disease Activity Index (CDAI) of 150 or less.
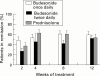
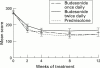
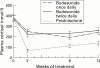
Results: After eight weeks of treatment, remission occurred in 60% of patients receiving budesonide once daily or prednisolone and in 42% of those receiving budesonide twice daily (p = 0.062). The presence of glucocorticoid associated side effects was similar in all groups; however, moon face was more common in the prednisolone group (p = 0.0005). The highest frequency of impaired adrenal function, as measured by a short ACTH test, was found in the prednisolone group (p = 0.0023).
Conclusions: Budesonide CIR, administered at 9 mg once daily or 4.5 mg twice daily, is comparable to prednisolone in inducing remission in active Crohn's disease. The single dose administration is as promptly effective as prednisolone and represents a simpler and safer therapeutic approach, with a considerable reduction in side effects.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of budesonide with prednisolone for active Crohn's disease.N Engl J Med. 1994 Sep 29;331(13):842-5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199409293311304. N Engl J Med. 1994. PMID: 8078530 Clinical Trial.
-
Budesonide versus prednisolone for the treatment of active Crohn's disease in children: a randomized, double-blind, controlled, multicentre trial.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 Jan;16(1):47-54. doi: 10.1097/00042737-200401000-00008. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 15095852 Clinical Trial.
-
Oral budesonide for active Crohn's disease. Canadian Inflammatory Bowel Disease Study Group.N Engl J Med. 1994 Sep 29;331(13):836-41. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199409293311303. N Engl J Med. 1994. PMID: 8078529 Clinical Trial.
-
Budesonide (Entocort EC Capsules): a review of its therapeutic use in the management of active Crohn's disease in adults.Drugs. 2002;62(15):2263-82. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262150-00015. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 12381231 Review.
-
Budesonide. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in inflammatory bowel disease.Drugs. 1995 Nov;50(5):854-72. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199550050-00006. Drugs. 1995. PMID: 8586030 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo evaluation of microparticulate drug delivery systems composed of macromolecular prodrugs.Molecules. 2008 Aug 10;13(9):2136-55. doi: 10.3390/molecules13092136. Molecules. 2008. PMID: 18830146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonabsorbable corticosteroids use in the treatment of gastrointestinal graft-versus-host disease.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009 Apr;15(4):395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2008.12.487. Epub 2009 Feb 10. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009. PMID: 19285626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagenous enterocolitis and maturity onset type 1 diabetes manifesting as uraemia, malabsorption and extreme weight loss.BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Jul 23;2014:bcr2013200409. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200409. BMJ Case Rep. 2014. PMID: 25056300 Free PMC article.
-
Aminosalicylates for induction of remission or response in Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 3;7(7):CD008870. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008870.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27372735 Free PMC article.
-
AGA Technical Review on the Medical Management of Moderate to Severe Luminal and Perianal Fistulizing Crohn's Disease.Gastroenterology. 2021 Jun;160(7):2512-2556.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.04.023. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 34051985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
