PARP is important for genomic stability but dispensable in apoptosis
- PMID: 9308963
- PMCID: PMC316515
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.18.2347
PARP is important for genomic stability but dispensable in apoptosis
Abstract
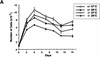
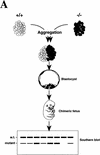
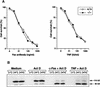
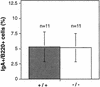
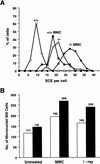
Mice lacking the gene encoding poly(ADP-ribosyl) transferase (PARP or ADPRT) display no phenotypic abnormalities, although aged mice are susceptible to epidermal hyperplasia and obesity in a mixed genetic background. Whereas embryonic fibroblasts lacking PARP exhibit normal DNA excision repair, they grow more slowly in vitro. Here we investigated the putative roles of PARP in cell proliferation, cell death, radiosensitivity, and DNA recombination, as well as chromosomal stability. We show that the proliferation deficiency in vitro and in vivo is most likely caused by a hypersensitive response to environmental stress. Although PARP is specifically cleaved during apoptosis, cells lacking this molecule apoptosed normally in response to treatment with anti-Fas, tumor neurosis factor alpha, gamma-irradiation, and dexamethasone, indicating that PARP is dispensable in apoptosis and that PARP-/- thymocytes are not hypersensitive to ionizing radiation. Furthermore, the capacity of mutant cells to carry out immunoglobulin class switching and V(D)J recombination is normal. Finally, primary PARP mutant fibroblasts and splenocytes exhibited an elevated frequency of spontaneous sister chromatid exchanges and elevated micronuclei formation after treatment with genotoxic agents, establishing an important role for PARP in the maintenance of genomic integrity.
Figures



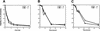
References
-
- Agarwal, M., A. Agarwal, W.R. Taylor, Z.-Q. Wang, E.F. Wagner, and G. Stark. 1997. Defective induction but normal activation and function of p53 in mouse cells lacking poly-ADP-ribose polymerase. Oncogene (in press). - PubMed
-
- Althaus FR, Richter C. ADP-ribosylation of proteins—Enzymology and biological significance. Mol Biol Biochem Biophys. 1987;37:1–125. - PubMed
-
- Catena C, Villani P, Conti D, Righi E. Micronuclei and 3AB index in X-irradiated human lymphocytes in G0 and G1 phases. Mutat Res. 1994;311:231–237. - PubMed
-
- Cleaver JE, Mitchell DL, Feeney L, Afzal V. Chromatid exchanges may be induced by damage in sites of transcriptional activity. Mutagenesis. 1996;11:183–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
