A beta-catenin/XTcf-3 complex binds to the siamois promoter to regulate dorsal axis specification in Xenopus
- PMID: 9308964
- PMCID: PMC316518
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.18.2359
A beta-catenin/XTcf-3 complex binds to the siamois promoter to regulate dorsal axis specification in Xenopus
Abstract
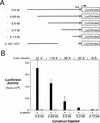
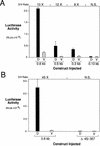
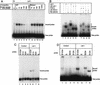
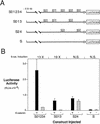
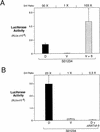
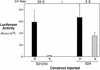
The Wnt pathway regulates the early dorsal-ventral axis in Xenopus through a complex of beta-catenin and HMG box transcription factors of the Lef/Tcf family. We show that the promoter of the dorsalizing homeo box gene siamois is a direct target for the beta-catenin/XTcf-3 complex, establishing a link between the Wnt pathway and the activation of genes involved in specifying the dorsal axis. By injecting siamois reporter constructs into the animal pole of Xenopus embryos, we show that a 0.8-kb fragment of the siamois promoter is strongly activated by beta-catenin. The proximal 0.5 kb, which is also activated by beta-catenin, contains three Lef/Tcf-binding sites. Mutations in these sites eliminate the beta-catenin-mediated activation of siamois and show that siamois is regulated by the beta-catenin/XTcf-3 complex, in combination with additional transcriptional activators. When expressed at the equator of the embryo, the siamois promoter is activated to much higher levels on the dorsal side than the ventral side. Ectopic ventral expression of beta-catenin raises the ventral expression of the siamois promoter to the dorsal levels. Conversely, ectopic dorsal expression of dominant-negative XTcf-3 abolishes the dorsal activation of the siamois promoter. Furthermore, elimination of the Lef/Tcf sites elevates the ventral expression of siamois, revealing a repressive role for XTcf-3 in the absence of beta-catenin. Finally, we find that the endogenous siamois activator, although present throughout the dorsal side of the embryo, is most potent in the dorsal vegetal region. We propose that the dorsal activation of siamois by the beta-catenin/XTcf-3 complex combined with the ventral repression of siamois by XTcf-3 results in the restriction of endogenous siamois expression to the dorsal side of Xenopus embryos.
Figures



References
-
- Bauer DV, Moody SA. The cleavage stage origin of Spemann’s organizer: Analysis of the movements of blastomere clones before and during gastrulation in Xenopus. Development. 1994;120:1179–1189. - PubMed
-
- Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kühl M, Bruhn L, Wedlich D, Grosschedl R, Birchmeier W. Functional interaction of β-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature. 1996;382:638–642. - PubMed
-
- Brannon M, Kimelman D. Activation of Siamois by the Wnt pathway. Dev Biol. 1996;180:344–347. - PubMed
-
- Brunner E, Peter O, Schweizer L, Basler K. pangolin encodes a Lef-1 homologue that acts downstream of Armadillo to transduce the Wingless signal in Drosophila. Nature. 1997;385:829–833. - PubMed
-
- Carnac G, Kodjabachian L, Gurdon JB, Lemaire P. The homeobox gene Siamois is a target of the Wnt dorsalization pathway and triggers organiser activity in the absence of mesoderm. Development. 1996;122:3055–3065. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
