Rpp1, an essential protein subunit of nuclear RNase P required for processing of precursor tRNA and 35S precursor rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 9308968
- PMCID: PMC316520
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.18.2414
Rpp1, an essential protein subunit of nuclear RNase P required for processing of precursor tRNA and 35S precursor rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Corrected and republished in
-
Rpp1, an essential protein subunit of nuclear RNase P required for processing of precursor tRNA and 35S precursor rRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Genes Dev. 1997 Nov 1;11(21):2926-37. doi: 10.1101/gad.11.21.2926. Genes Dev. 1997. PMID: 9353260 Free PMC article.
Abstract
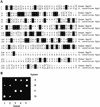
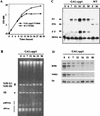
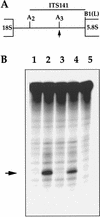
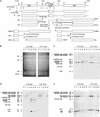
The gene for an essential protein subunit of nuclear RNase P from Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been cloned. The gene for this protein, RPP1, was identified by virtue of its homology with a human scleroderma autoimmune antigen, Rpp30, which copurifies with human RNase P. Epitope-tagged Rpp1 can be found in association with both RNase P RNA and a related endoribonuclease, RNase MRP RNA, in immunoprecipitates from crude extracts of cells. Depletion of Rpp1 in vivo leads to the accumulation of precursor tRNAs with unprocessed 5' and 3' termini and reveals rRNA processing defects that have not been described previously for proteins associated with RNase P or RNase MRP. Immunoprecipitated complexes cleave both yeast precursor tRNAs and precursor rRNAs.
Figures



References
-
- Alifano P, Rivellini F, Piscitelli C, Arraiano CM, Bruni CB, Carlomagno MS. Ribonuclease E provides substrates for ribonuclease P-dependent processing of a polycistronic mRNA. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:3021–3031. - PubMed
-
- Altman S, Kirseborm L, Talbot S. Recent studies of ribonuclease P. FASEB J. 1993;7:7–14. - PubMed
-
- ————— . Recent studies of RNase P. In: Soll D, RajBhandary UL, editors. tRNA: Structure biosynthesis and function. Washington, DC.: American Society for Microbiology; 1995. pp. 67–78.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
