Required early complement activation in contact sensitivity with generation of local C5-dependent chemotactic activity, and late T cell interferon gamma: a possible initiating role of B cells
- PMID: 9314551
- PMCID: PMC2199060
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.186.7.1015
Required early complement activation in contact sensitivity with generation of local C5-dependent chemotactic activity, and late T cell interferon gamma: a possible initiating role of B cells
Abstract
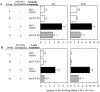
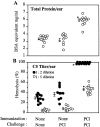
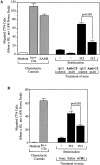
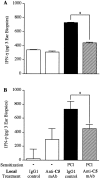
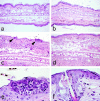
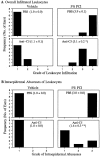
Complement (C) is an important component of innate immunity, and was also shown recently to participate in induction of acquired B cell humoral immunity. In this study, we present evidence that C also participates in acquired T cell immunity. We found that C was involved in early events of the efferent elicitation phase of contact sensitivity (CS), and delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH). Thus, CS and DTH were inhibited by administration of a C-blocker, soluble recombinant C receptor-1 (sCR1), when given 30 min before, but not 3 h after local antigen challenge. Among C components, local C5 were thought crucial to elicitation of CS, since local administration of anti-C5 monoclonal antibodies or locally injected C-depleting cobra venom factor also inhibited CS and DTH. These findings were consistent with our previous finding of the importance of C5 for CS elicitation, using congenitally C5-deficient mice. To dissect the mechanism of C dependence in CS, we demonstrated that locally increased early macrophage chemotactic activity (probably C5a) in evolving CS skin extracts, as well as late elaboration of IFN-gamma, were both inhibited by anti-C treatment. In addition, histological analysis showed that leukocyte recruitment into CS ear sites was similarly C-dependent. Furthermore, an initiating role of B cell-derived C-fixing immunoglobulin was suggested by demonstration of impaired CS responses in B cell-deficient mice. In summary, these results suggest that C was activated locally, perhaps via a B cell product, in an important early component of the stepwise events necessary to elicit CS, leading to local production of C5-dependent macrophage chemotactic activity and later IFN-gamma, and subsequently leading to cell infiltration, for development of T cell-dependent CS.
Figures
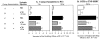
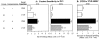
Similar articles
-
B cell-dependent T cell responses: IgM antibodies are required to elicit contact sensitivity.J Exp Med. 2002 Nov 18;196(10):1277-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020649. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12438420 Free PMC article.
-
Early local generation of C5a initiates the elicitation of contact sensitivity by leading to early T cell recruitment.J Immunol. 2000 Aug 1;165(3):1588-98. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.3.1588. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10903768
-
B-1 B cell IgM antibody initiates T cell elicitation of contact sensitivity.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000;252:171-7. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-57284-5_18. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11125474 Review.
-
Possible involvement of C5/C5a in the efferent and elicitation phases of contact sensitivity.J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4444-50. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8648091
-
Yes T cells, but three different T cells (alphabeta, gammadelta and NK T cells), and also B-1 cells mediate contact sensitivity.Clin Exp Immunol. 2001 Sep;125(3):345-50. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01619.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11531940 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
B cell-dependent T cell responses: IgM antibodies are required to elicit contact sensitivity.J Exp Med. 2002 Nov 18;196(10):1277-90. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020649. J Exp Med. 2002. PMID: 12438420 Free PMC article.
-
Antiviral treatment down-regulates peripheral B-cell CD81 expression and CD5 expansion in chronic hepatitis C virus infection.J Virol. 2003 Oct;77(19):10432-6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.19.10432-10436.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12970428 Free PMC article.
-
Topical tacrolimus and cyclosporin A differentially inhibit early and late effector phases of cutaneous delayed-type and immunoglobulin E hypersensitivity.Immunology. 2001 Oct;104(2):235-42. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2001.01288.x. Immunology. 2001. PMID: 11683964 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the complement anaphylatoxin receptor C5L2 exacerbates inflammation in allergic contact dermatitis.J Immunol. 2013 Oct 15;191(8):4001-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301626. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24043888 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody-enhanced cross-presentation of self antigen breaks T cell tolerance.J Clin Invest. 2007 May;117(5):1361-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI29470. Epub 2007 Apr 19. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17446931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fearon DT, Locksley RM. The instructive role of innate immunity in the acquired immune response. Science (Wash DC) 1996;272:50–54. - PubMed
-
- Scharton-Kersten T, Scott P. The role of the innate immune response in Th1 cell development following Leishmania majorinfection. J Leukocyte Biol. 1995;57:515–522. - PubMed
-
- Hsieh CS, Macatonia SE, Tripp CS, Wolf SF, O'Garra A, Murphy KM. Development of TH1 CD4+ T cells through IL-12 produced by Listeria-induced macrophages. Science (Wash DC) 1993;260:547–549. - PubMed
-
- Bendelac A. Mouse NK1+T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:367–374. - PubMed
-
- Dempsey PW, Allison MED, Akkaraju S, Goodnow CC, Fearon DT. C3d of complement as molecular adjuvant: bridging innate and acquired immunity. Science (Wash DC) 1996;271:348–350. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

