Identification of a cellular receptor for subgroup E avian leukosis virus
- PMID: 9326659
- PMCID: PMC23555
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.21.11617
Identification of a cellular receptor for subgroup E avian leukosis virus
Abstract
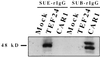
Genetic studies in chickens and receptor interference experiments have indicated that avian leukosis virus (ALV)-E may utilize a cellular receptor related to the receptor for ALV-B and ALV-D. Recently, we cloned CAR1, a tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR)-related protein, that serves as a cellular receptor for ALV-B and ALV-D. To determine whether the cellular receptor for ALV-E is a CAR1-like protein, a cDNA library was made from turkey embryo fibroblasts (TEFs), which are susceptible to ALV-E infection, but not to infection by ALV-B and ALV-D. The cDNA library was screened with a radioactively labeled CAR1 cDNA probe, and clones that hybridized with the probe were isolated. A 2.3-kb cDNA clone was identified that conferred susceptibility to ALV-E infection, but not to ALV-B infection, when expressed in transfected human 293 cells. The functional cDNA clone is predicted to encode a 368 amino acid protein with significant amino acid similarity to CAR1. Like CAR1, the TEF protein is predicted to have two extracellular TNFR-like cysteine-rich domains and a putative death domain similar to those of TNFR I and Fas. Flow cytometric analysis and immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated specific binding between the TEF CAR1-related protein and an immunoadhesin composed of the surface (SU) envelope protein of subgroup E (RAV-0) virus fused to the constant region of a rabbit immunoglobulin. These two activities of the TEF CAR1-related protein, specific binding to ALV-E SU and permitting entry only of ALV-E, have unambiguously identified this protein as a cellular receptor specific for subgroup E ALV.
Figures



References
-
- Weiss R A. In: The Retroviridae. Levy J A, editor; Levy J A, editor. New York: Plenum; 1993. pp. 1–107.
-
- Hernandez L D, Hoffman L R, Wolfsberg T G, White J M. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1996;12:627–661. - PubMed
-
- Crittenden L B, Wendel E J, Motta J V. Virology. 1973;52:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Crittenden L B, Motta J V. Virology. 1975;67:327–334. - PubMed
-
- Brojatsch J, Naughton J, Rolls M M, Zingler Z, Young J A T. Cell. 1996;87:845–855. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

