Translational repressor bruno plays multiple roles in development and is widely conserved
- PMID: 9334316
- PMCID: PMC316560
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.19.2510
Translational repressor bruno plays multiple roles in development and is widely conserved
Abstract
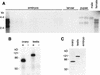
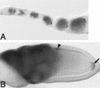
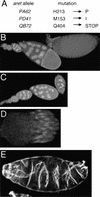
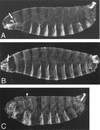
oskar (osk) mRNA is tightly localized to the posterior pole of the Drosophila oocyte, where the subsequent expression of Osk protein directs abdomen and germ-line formation in the developing embryo. Misplaced expression of Osk protein leads to lethal body patterning defects. The Osk message is translationally repressed before and during the localization process, ensuring that Osk protein is only expressed after the mRNA has reached the posterior. An ovarian protein, Bruno (Bru), has been implicated as a translational repressor of osk mRNA. Here we report the isolation of a cDNA encoding Bru using a novel approach to the expression cloning of an RNA-binding protein, and the identification of previously described mutants in the arrest (aret)-locus as mutants in Bru. The mutant phenotype, along with the binding properties of the protein and its pattern of accumulation within the oocyte, indicate that Bru regulates multiple mRNAs involved in female and male gametogenesis as well as early in embryogenesis. Genetic experiments provide further evidence that Bru functions in the translational repression of osk. Intriguingly, we find that Bru interacts physically with Vasa (Vas), an RNA helicase that is a positive regulator of osk translation. Bru belongs to an evolutionarily conserved family of genes, suggesting that Bru-mediated translational regulation may be widespread. Models for the molecular mechanism of Bru function are discussed.
Figures


References
-
- Bandziulis RJ, Swanson MS, Dreyfuss G. RNA-binding proteins as developmental regulators. Genes & Dev. 1989;3:431–437. - PubMed
-
- Bass BL, Hurst SR, Singer JD. Binding properties of newly identified Xenopus proteins containing dsRNA-binding motifs. Curr Biol. 1994;4:301–314. - PubMed
-
- Bouvet P, Omilli F, Arlot-Bonnemains Y, Legagneux V, Roghi C, Bassez T, Osborne HB. The deadenylation conferred by the 3′ untranslated region of a developmentally controlled mRNA in Xenopus embryos is switched to polyadenylation by deletion of a short sequence element. Mol Cell Biol. 1994;14:1893–1900. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Castrillon DH, Gönczy P, Alexander S, Rawson R, Eberhart CG, Viswanathan S, DiNardo S, Wasserman SA. Toward a molecular genetic analyis of spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: Characterization of male-sterile mutants generated by single P element mutagenesis. Genetics. 1993;135:489–505. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christerson LB, McKearin DM. orb is required for anteroposterior and dorsoventral patterning during Drosophila oogenesis. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:614–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
