Topoisomerase IV, not gyrase, decatenates products of site-specific recombination in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 9334322
- PMCID: PMC316566
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.19.2580
Topoisomerase IV, not gyrase, decatenates products of site-specific recombination in Escherichia coli
Abstract
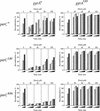
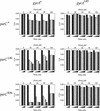
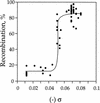
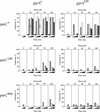
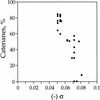
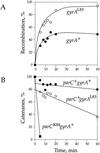
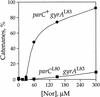
DNA replication and recombination generate intertwined DNA intermediates that must be decatenated for chromosome segregation to occur. We showed recently that topoisomerase IV (topo IV) is the only important decatenase of DNA replication intermediates in bacteria. Earlier results, however, indicated that DNA gyrase has the primary role in unlinking the catenated products of site-specific recombination. To address this discordance, we constructed a set of isogenic strains that enabled us to inhibit selectively with the quinolone norfloxacin topo IV, gyrase, both enzymes, or neither enzyme in vivo. We obtained identical results for the decatenation of the products of two different site-specific recombination enzymes, phage lambda integrase and transposon Tn3 resolvase. Norfloxacin blocked decatenation in wild-type strains, but had no effect in strains with drug-resistance mutations in both gyrase and topo IV. When topo IV alone was inhibited, decatenation was almost completely blocked. If gyrase alone were inhibited, most of the catenanes were unlinked. We showed that topo IV is the primary decatenase in vivo and that this function is dependent on the level of DNA supercoiling. We conclude that the role of gyrase in decatenation is to introduce negative supercoils into DNA, which makes better substrates for topo IV. We also discovered that topo IV has an unexpectedly strong DNA relaxation activity that, together with gyrase and topo I, is able to set the supercoiling levels in Escherichia coli.
Figures


References
-
- Adams DE, Bliska JB, Cozzarelli NR. Cre-lox recombination in E. coli cells: Mechanistic differences from the in vitro reaction. J Mol Biol. 1992a;226:661–673. - PubMed
-
- Adams DE, Shekhtman EM, Zechiedrich EL, Schmid MB, Cozzarelli NR. The role of topoisomerase IV in partitioning bacterial replicons and the structure of catenated intermediates in DNA replication. Cell. 1992b;71:277–288. - PubMed
-
- Belland RJ, Morrison SG, Ison C, Huang WM. Neisseria gonorrhoeae acquires mutations in analogous regions of gyrA and parC in fluoroquinolone-resistant isolates. Mol Microbiol. 1994;14:371–380. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin KR, Abola AP, Kanaar R, Cozzarelli NR. Contributions of supercoiling to Tn3 resolvase and phage mu gin site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1996;256:50–65. - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti M-A. DNA topoisomerases. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1991;1:99–103.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
