The DAF-3 Smad protein antagonizes TGF-beta-related receptor signaling in the Caenorhabditis elegans dauer pathway
- PMID: 9334330
- PMCID: PMC316611
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.11.20.2679
The DAF-3 Smad protein antagonizes TGF-beta-related receptor signaling in the Caenorhabditis elegans dauer pathway
Abstract
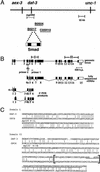
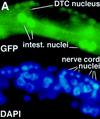
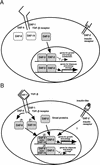
Signals from TGF-beta superfamily receptors are transduced to the nucleus by Smad proteins, which transcriptionally activate target genes. In Caenorhabditis elegans, defects in a TGF-beta-related pathway cause a reversible developmental arrest and metabolic shift at the dauer larval stage. Null mutations in daf-3 suppress mutations in genes encoding this TGF-beta signal, its receptors, and associated Smad signal transduction proteins. daf-3 encodes a Smad protein that is most closely related to mammalian DPC4, and is expressed throughout development in many of the tissues that are remodeled during dauer development. DAF-4, the type II TGF-beta receptor in this pathway, is also expressed in remodeled tissues. These data suggest that the DAF-7 signal from sensory neurons acts as a neuroendocrine signal throughout the body to directly regulate developmental and metabolic shifts in tissues that are remodeled during dauer formation. A full-length functional DAF-3/GFP fusion protein is predominantly cytoplasmic, and this localization is independent of activity of the upstream TGF-beta-related pathway. However, this fusion protein is associated with chromosomes in mitotic cells, suggesting that DAF-3 binds DNA directly or indirectly. DAF-3 transgenes also interfere with dauer formation, perhaps attributable to a dosage effect. A truncated DAF-3/GFP fusion protein that is predominantly nuclear interferes with dauer formation, implying a role for DAF-3 in the nucleus. These data suggest that DAF-7 signal transduction antagonizes or modifies DAF-3 Smad activity in the nucleus to induce reproductive development; when DAF-7 signals are disabled, unmodified DAF-3 Smad activity mediates dauer arrest and its associated metabolic shift. Therefore, daf-3 is unique in that it is antagonized, rather than activated, by a TGF-beta pathway.
Figures




References
-
- Attisano L, Wrana JL, Montalvo E, Massague J. TGF-β receptors and actions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994;1222:71–80. - PubMed
-
- Baker JC, Harland RM. A novel mesoderm inducer, Madr2, functions in the activin signal transduction pathway. Genes & Dev. 1996;10:1880–1889. - PubMed
-
- Bargmann CI, Horvitz HR. Control of larval development by chemosensory neurons in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 1991;251:1243–1246. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prasher DC. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 1994;263:802–805. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Rubrock M, Whitman M. A transcriptional partner for MAD proteins in TGF-β signaling. Nature. 1996;383:691–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
