Developmental expression pattern of phototransduction components in mammalian pineal implies a light-sensing function
- PMID: 9334383
- PMCID: PMC6573733
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-21-08074.1997
Developmental expression pattern of phototransduction components in mammalian pineal implies a light-sensing function
Abstract
Whereas the pineal organs of lower vertebrates have been shown to be photosensitive, photic regulation of pineal function in adult mammals is thought be mediated entirely by retinal photoreceptors. Extraretinal regulation of pineal function has been reported in neonatal rodents, although both the site and molecular basis of extraretinal photoreception have remained obscure. In this study we examine the developmental expression pattern of all of the principal components of retinal phototransduction in rat pineal via cRNA in situ hybridization. All of the components needed to reconstitute a functional phototransduction pathway are expressed in the majority of neonatal pinealocytes, although the expression levels of many of these genes decline dramatically during development. These findings strongly support the theory that the neonatal rat pineal itself is photosensitive. In addition, we observe in neonatal pinealocytes the expression of both rod-specific and cone-specific phototransduction components, implying the existence of functionally different subtypes of pinealocytes that express varying combinations of phototransduction enzymes.
Figures
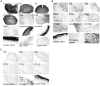
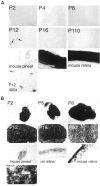
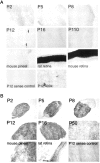


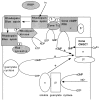
Similar articles
-
Molecular evidence that human ocular ciliary epithelium expresses components involved in phototransduction.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001 Jun 8;284(2):317-25. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.4970. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001. PMID: 11394879
-
Developmental patterns of protein expression in photoreceptors implicate distinct environmental versus cell-intrinsic mechanisms.Vis Neurosci. 2001 Jan-Feb;18(1):157-68. doi: 10.1017/s0952523801181150. Vis Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11347813
-
Recoverin in pineal organs and retinae of various vertebrate species including man.Brain Res. 1992 Nov 6;595(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)91452-k. Brain Res. 1992. PMID: 1467959
-
Photoreceptor-specific proteins in the mammalian pineal organ: immunocytochemical data and functional considerations.Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 1994;54 Suppl:9-17. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 1994. PMID: 7528460 Review.
-
Recoverin and rhodopsin kinase.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;514:101-7. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0121-3_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12596917 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of photosensitivity in neonatal rat pineal gland.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Oct 10;97(21):11540-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.210248297. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11005846 Free PMC article.
-
Dim Light at Night and Constant Darkness: Two Frequently Used Lighting Conditions That Jeopardize the Health and Well-being of Laboratory Rodents.Front Neurol. 2018 Aug 2;9:609. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00609. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30116218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In silico characterisation and chromosomal localisation of human RRH (peropsin)--implications for opsin evolution.BMC Genomics. 2003 Jan 24;4(1):3. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-4-3. Epub 2003 Jan 24. BMC Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12542842 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-related receptor β deficiency alters body composition and response to restraint stress.BMC Physiol. 2013 Sep 22;13:10. doi: 10.1186/1472-6793-13-10. BMC Physiol. 2013. PMID: 24053666 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of the microRNA-183/96/182 cluster results in syndromic retinal degeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 5;110(6):E507-16. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1212655110. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23341629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamus G, Palczewski K, Carruth M, McDowell JH, Hargrave PA. Visual transduction system in the rat pineal gland: evidence for rhodopsin and rhodopsin kinase. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Suppl] 1989;30:284.
-
- Araki M. Cellular mechanism for norepinephrine suppression of pineal photoreceptor-like cell differentiation in rat pineal cultures. Dev Biol. 1992;149:440–447. - PubMed
-
- Baehr W, Champagne MS, Lee AK, Pittler SJ. Complete cDNA sequences of mouse rod photoreceptor cGMP phosphodiesterase alpha- and beta-subunits and identification of beta′, a putative beta-subunit isozyme produced by alternative splicing of the beta-subunit gene. FEBS Lett. 1991;278:107–114. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barnstable CJ, Morabito MR. Isolation and coding sequence of the rat rod opsin gene. J Mol Neurosci. 1994;5:207–209. - PubMed
-
- Barr L. Photomechanical coupling in the vertebrate sphincter pupillae. CRC Crit Rev Neurosci. 1989;4:325–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
