Developmental synaptic depression underlying reorganization of visceral reflex pathways in the spinal cord
- PMID: 9334413
- PMCID: PMC6573738
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-21-08402.1997
Developmental synaptic depression underlying reorganization of visceral reflex pathways in the spinal cord
Abstract
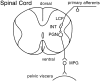
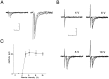
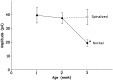
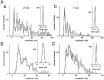
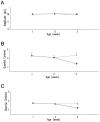
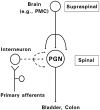
During development, neuronal connectivity has a remarkable plasticity. Synaptic refinement in the spinal autonomic nucleus might be involved in the elimination of primitive segmental reflexes and the emergence of mature spinobulbospinal reflexes, which occurs a few weeks after birth. To address this possibility, we examined the postnatal changes of segmental excitatory synaptic transmission by applying the whole-cell recording technique to parasympathetic preganglionic neurons in slice preparations of the rat lumbosacral spinal cord. The mean magnitude of unitary excitatory synaptic currents evoked in preganglionic neurons by stimulation of single interneurons remained unchanged during the first two postnatal weeks but was reduced by 50% during the third postnatal week. This reduction in synaptic efficacy was associated with a decrease in the amount of transmitter release from interneurons. Moreover, this developmental depression of segmental synaptic transmission was prevented by spinal cord transection at the thoracic level on postnatal day 14. Thus, developmental modification of excitatory synapses on preganglionic neurons appears to be attributable to competition between segmental interneuronal and descending bulbospinal inputs, which results in the developmental reorganization of parasympathetic excretory reflex pathways.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson CR, Edwards SL. Intraperitoneal injections of fluorogold reliably labels all sympathetic preganglionic neurons in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 1994;53:137–141. - PubMed
-
- Araki I. Inhibitory postsynaptic currents and the effects of GABA on visually identified sacral parasympathetic preganglionic neurons in neonatal rats. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:2903–2910. - PubMed
-
- Araki I, de Groat WC. Unitary excitatory synaptic currents in preganglionic neurons mediated by two distinct groups of interneurons in neonatal rat sacral parasympathetic nucleus. J Neurophysiol. 1996;76:215–226. - PubMed
-
- Balice-Gorden RJ, Lichtman JW. Long-term synapse loss induced by focal blockade of postsynaptic receptors. Nature. 1994;372:519–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
