Rhinal cortex removal produces amnesia for preoperatively learned discrimination problems but fails to disrupt postoperative acquisition and retention in rhesus monkeys
- PMID: 9334426
- PMCID: PMC6573729
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-21-08536.1997
Rhinal cortex removal produces amnesia for preoperatively learned discrimination problems but fails to disrupt postoperative acquisition and retention in rhesus monkeys
Abstract
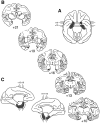
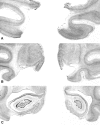
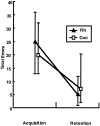
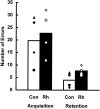
To test whether the rhinal cortex (i.e., entorhinal and perirhinal cortex) plays a time-limited role in information storage, eight rhesus monkeys were trained to criterion on two sets of 60 object discrimination problems, one set at each of two different time periods separated by 15 weeks. After the monkeys had learned both sets, two groups balanced for preoperative acquisition rates were formed. One group received bilateral ablation of the rhinal cortex (n = 4), and the other was retained as an unoperated control group (n = 4). After a 2 week rest period, monkeys were assessed for retention of the object discrimination problems. Retention was significantly poorer in monkeys with removals of the rhinal cortex relative to the controls (68 vs 91%). Although both groups showed slightly better retention of problems from the more recently learned set, there was no evidence of a differential effect of the cortical removal across sets (i.e., no temporal gradient). In addition, the monkeys with rhinal cortex lesions subsequently learned three new sets of 10 object discrimination problems as quickly as the controls did, thus ruling out the possibility of a gross impairment in visual perception or discrimination abilities. Furthermore, they retained these postoperatively learned object discriminations as well as the controls did. The findings indicate that the rhinal cortex is critical for the storage and/or retrieval of object discrimination problems that were learned up to 16 weeks before rhinal cortex ablation; however, in the absence of the rhinal cortex, efficient learning and retention of new discrimination problems can still occur.
Figures
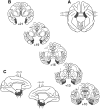
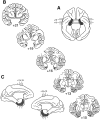
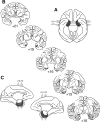
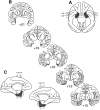




Similar articles
-
Impairments in visual discrimination learning and recognition memory produced by neurotoxic lesions of rhinal cortex in rhesus monkeys.Eur J Neurosci. 2001 Mar;13(6):1228-38. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01491.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11285020
-
Rhinal cortex lesions produce mild deficits in visual discrimination learning for an auditory secondary reinforcer in rhesus monkeys.Behav Neurosci. 1999 Apr;113(2):243-52. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.113.2.243. Behav Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10357449
-
Rhinal cortex, but not medial thalamic, lesions cause retrograde amnesia for objects in rats.Neuroreport. 1999 Sep 9;10(13):2853-8. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199909090-00028. Neuroreport. 1999. PMID: 10511452
-
Preserved recognition memory for small sets, and impaired stimulus identification for large sets, following rhinal cortex ablations in monkeys.Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Sep 1;6(9):1466-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb01008.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1994. PMID: 8000570
-
Monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) with rhinal cortex ablations succeed in object discrimination learning despite 24-hr intertrial intervals and fail at matching to sample despite double sample presentations.Behav Neurosci. 1992 Feb;106(1):30-8. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.106.1.30. Behav Neurosci. 1992. PMID: 1554436
Cited by
-
Interaction between perirhinal and medial prefrontal cortex is required for temporal order but not recognition memory for objects in rats.J Neurosci. 2004 May 12;24(19):4596-604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5517-03.2004. J Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15140931 Free PMC article.
-
Selective perceptual impairments after perirhinal cortex ablation.J Neurosci. 2001 Dec 15;21(24):9824-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-24-09824.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11739590 Free PMC article.
-
Ventral striatum lesions do not affect reinforcement learning with deterministic outcomes on slow time scales.Behav Neurosci. 2017 Oct;131(5):385-91. doi: 10.1037/bne0000211. Epub 2017 Aug 14. Behav Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28805428 Free PMC article.
-
The Rhesus Monkey Hippocampus Critically Contributes to Scene Memory Retrieval, But Not New Learning.J Neurosci. 2018 Sep 5;38(36):7800-7808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0832-18.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 26. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30049888 Free PMC article.
-
Perirhinal cortex removal dissociates two memory systems in matching-to-sample performance in rhesus monkeys.J Neurosci. 2011 Nov 9;31(45):16336-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2338-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22072685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggleton JP, Mishkin M. Projections of the amygdala to the thalamus in the cynomolgus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1984;222:56–68. - PubMed
-
- Bolhuis JJ, Stewart CA, Forrest EM (1994) Retrograde amnesia and memory reactivation in rats with ibotenate lesions to the hippocampus or subiculum. Q J Exp Psychol 47[B]:129–150. - PubMed
-
- Buckley MJ, Gaffan D. Impairment of visual object-discrimination learning after perirhinal cortex ablation. Behav Neurosci. 1997;111:467–475. - PubMed
-
- Cho YH, Kesner RP. Involvement of entorhinal cortex or parietal cortex in long-term spatial discrimination memory in rats: retrograde amnesia. Behav Neurosci. 1996;110:436–442. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
