The amino-terminal region of Tyk2 sustains the level of interferon alpha receptor 1, a component of the interferon alpha/beta receptor
- PMID: 9342324
- PMCID: PMC23625
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.94.22.11839
The amino-terminal region of Tyk2 sustains the level of interferon alpha receptor 1, a component of the interferon alpha/beta receptor
Abstract
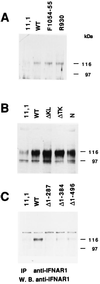
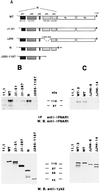
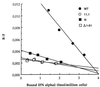
Tyk2 belongs to the Janus kinase (JAK) family of receptor associated tyrosine kinases, characterized by a large N-terminal region, a kinase-like domain and a tyrosine kinase domain. It was previously shown that Tyk2 contributes to interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) signaling not only catalytically, but also as an essential intracellular component of the receptor complex, being required for high affinity binding of IFN-alpha. For this function the tyrosine kinase domain was found to be dispensable. Here, it is shown that mutant cells lacking Tyk2 have significantly reduced IFN-alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) protein level, whereas the mRNA level is unaltered. Expression of the N-terminal region of Tyk2 in these cells reconstituted wild-type IFNAR1 level, but did not restore the binding activity of the receptor. Studies of mutant Tyk2 forms deleted at the N terminus indicated that the integrity of the N-terminal region is required to sustain IFNAR1. These studies also showed that the N-terminal region does not directly modulate the basal autophosphorylation activity of Tyk2, but it is required for efficient in vitro IFNAR1 phosphorylation and for rendering the enzyme activatable by IFN-alpha. Overall, these results indicate that distinct Tyk2 domains provide different functions to the receptor complex: the N-terminal region sustains IFNAR1 level, whereas the kinase-like domain provides a function toward high affinity ligand binding.
Figures

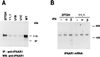
References
-
- Ihle J N. Adv Immunol. 1995;60:1–35. - PubMed
-
- Leaman D W, Leung S, Li X, Stark G R. FASEB J. 1996;10:1578–1588. - PubMed
-
- Velazquez L, Fellous M, Stark G R, Pellegrini S. Cell. 1992;70:313–322. - PubMed
-
- Müller M, Briscoe J, Laxton C, Guschin D, Ziemiecki A, Silvennoinen O, Harpur A G, Barbieri G, Witthuhn B A, Schindler C, Pellegrini S, Wilks A F, Ihle J N, Stark G R, Kerr I M. Nature (London) 1993;366:129–166. - PubMed
-
- Uzé G, Luftalla G, Gresser I. Cell. 1990;60:225–234. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

