GABAergic disinhibition changes the recovery cycle of bat inferior collicular neurons
- PMID: 9342856
- PMCID: PMC2862906
- DOI: 10.1007/s003590050119
GABAergic disinhibition changes the recovery cycle of bat inferior collicular neurons
Abstract
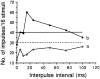
This study examines the contribution of GABAergic inhibition to the discharge pattern and recovery properties of 110 bat inferior collicular neurons by means of bicuculline application to their recording sites. When stimulated with single pulses, 74 (67%) neurons discharged one or two impulses (phasic responders), 19 (17%) discharged three to ten impulses (phasic bursters) and 17 (16%) discharged impulses throughout the entire stimulus duration (tonic responders). Bicuculline application changed phasic responders into phasic bursters or tonic responders, increased the number of impulses by 10-2000% and shortened the response latency of most neurons. When stimulated with pairs of sound pulses, the recovery cycles of these neurons can be described as: (1) long inhibition (n = 49, 45%); (2) short inhibition (n = 41, 37%); and (3) fast recovery (n = 20, 18%) based upon the 50% recovery time that was either longer than 20 ms, between 10 and 20 ms or shorter than 10 ms. Bicuculline application shortened the 50% recovery time of most neurons by 11-2350% allowing them to respond to pairs of sound pulses at very short interpulse intervals. These data demonstrate that GABAergic inhibition contributes significantly to auditory temporal processing.
Figures







References
-
- Adams JC. Ascending projections to the inferior colliculus. J Comp Neurol. 1979;183:519–538. - PubMed
-
- Adams JC, Mugnaini E. Dorsal nucleus of the lateral lemniscus: a nucleus of GABAergic projection neurons. Brain Res Bull. 1984;13:585–590. - PubMed
-
- Aitkin LM, Prain SM. Medial geniculate body: unit responses in awake cats. J Neurophysiol. 1974;37:512–521. - PubMed
-
- Bormann J. Electrophysiology of GABAA and GABAB receptor subtypes. Trend Neurosci. 1988;11:112–116. - PubMed
-
- Casseday JH, Covey E. Frequency tuning properties of neurons in the inferior colliculus of an FM bat. J Comp Neurol. 1992;319:34–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
