Characterization of the Golgi complex cleared of proteins in transit and examination of calcium uptake activities
- PMID: 9348533
- PMCID: PMC25639
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.8.10.1911
Characterization of the Golgi complex cleared of proteins in transit and examination of calcium uptake activities
Abstract
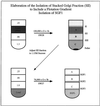
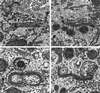
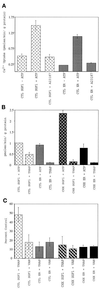
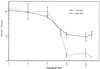
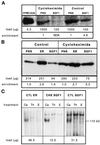
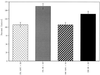
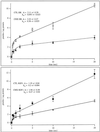
To characterize endogenous molecules and activities of the Golgi complex, proteins in transit were > 99% cleared from rat hepatocytes by using cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. The loss of proteins in transit resulted in condensation of the Golgi cisternae and stacks. Isolation of a stacked Golgi fraction is equally efficient with or without proteins in transit [control (CTL SGF1) and cycloheximide (CHX SGF1)]. Electron microscopy and morphometric analysis showed that > 90% of the elements could be positively identified as Golgi stacks or cisternae. Biochemical analysis showed that the cis-, medial-, trans-, and TGN Golgi markers were enriched over the postnuclear supernatant 200- to 400-fold with and 400- to 700-fold without proteins in transit. To provide information on a mechanism for import of calcium required at the later stages of the secretory pathway, calcium uptake into CTL SGF1 and CHX SGF1 was examined. All calcium uptake into CTL SGF1 was dependent on a thapsigargin-resistant pump not resident to the Golgi complex and a thapsigargin-sensitive pump resident to the Golgi. Experiments using CHX SGF1 showed that the thapsigargin-resistant activity was a plasma membrane calcium ATPase isoform in transit to the plasma membrane and the thapsigargin-sensitive pump was a sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase isoform. In vivo both of these calcium ATPases function to maintain millimolar levels of calcium within the Golgi lumen.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Kinetic characterization of calcium uptake by the rat liver Golgi apparatus.Cell Biol Int. 2000;24(4):229-33. doi: 10.1006/cbir.2000.0496. Cell Biol Int. 2000. PMID: 10816324
-
Two-dimensional mapping of the endogenous proteins of the rat hepatocyte Golgi complex cleared of proteins in transit.Electrophoresis. 1997 Dec;18(14):2601-12. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150181416. Electrophoresis. 1997. PMID: 9527490
-
The SPCA1 Ca2+ pump and intracellular membrane trafficking.Traffic. 2010 Oct;11(10):1315-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01096.x. Traffic. 2010. PMID: 20604898
-
Microscopic morphology and the origins of the membrane maturation model of Golgi apparatus function.Int Rev Cytol. 2007;262:191-218. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(07)62004-X. Int Rev Cytol. 2007. PMID: 17631189 Review.
-
Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum-Ca-ATPase by glycolysis in eukaryotic cells.Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1996;22(5-6):318-35. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1996. PMID: 8933503 Review.
Cited by
-
A putative calcium-ATPase of the secretory pathway family may regulate calcium/manganese levels in the Golgi apparatus of Entamoeba histolytica.Parasitol Res. 2018 Nov;117(11):3381-3389. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-6030-4. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 30084034
-
The Golgi apparatus is a functionally distinct Ca2+ store regulated by the PKA and Epac branches of the β1-adrenergic signaling pathway.Sci Signal. 2015 Oct 13;8(398):ra101. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa7677. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26462734 Free PMC article.
-
A thapsigargin-sensitive Ca(2+) pump is present in the pea Golgi apparatus membrane.Plant Physiol. 2002 Aug;129(4):1820-8. doi: 10.1104/pp.002055. Plant Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12177495 Free PMC article.
-
Progestin modulates the lipid profile and sensitivity of breast cancer cells to docetaxel.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012 Nov 5;363(1-2):111-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2012.08.005. Epub 2012 Aug 16. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22922095 Free PMC article.
-
GOLAC: an endogenous anion channel of the Golgi complex.Biophys J. 2000 Jun;78(6):2918-28. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76832-9. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 10827972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumrucker CR, Keenan TW. Membranes of mammary gland. X. Adenosine triphosphate dependent calcium accumulation by Golgi apparatus rich fractions from bovine mammary gland. Exp Cell Res. 1975;90:253–260. - PubMed
-
- Beaufay H, Amar-Costesec A, Feytmans E, Thines-Sempoux D, Wibo M, Robbi M, Berthet J. Analytical study of microsomes and isolated subcellular membranes from rat liver. 3. Subfractionation of the microsomal fraction by isopycnic and differential centrifugation in density gradients. J Cell Biol. 1974;61:188–200. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berger EG, Mandel TH, Schilt U. Immunohistochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in human fibroblasts and HeLa cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981;29:364–371. - PubMed
-
- Bergeron JJM. Golgi fractions from livers of control and ethanol-intoxicated rats. Enzymic and morphologic properties following rapid isolation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979;555:493–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

